Automotive Linear Regulators M
a CAN driver or other bus-interface device with minor analog circuitry connected to it. It might draw 150mA of supply current in full operation.
A linear regulator with 13V nominal input voltage can, therefore, dissipate 1.2W, and that level can rise briefly to 4W during a load dump. To handle the nominal 26V found in a truck, the regulator must dissipate more than 3W continuously. For these applications, another automotive linear regulator (MAX5087) has been designed for output currents as large as 400mA. It also comes in a larger 8mm x 8mm, 56-pin QFN package that boosts the allowable power dissipation to 3.8W (Figure 5).
Figure 5. One package option for the MAX5087 linear regulator is a 56-pin QFN, which increases its maximum allowable power dissipation to 3.8W.
For applications that require "housekeeping" features, the best choice is a MAX6791 linear regulator (Figure 6). Its 20-pin QFN package can dissipate 2.7W, and one of its dual linear regulators can generate a second supply voltage: 3.3V for a microprocessor and 5V for a CAN transceiver, for example. Other features include a watchdog with programmable trigger window, a power-on reset, a power-fail comparator for monitoring an additional supply voltage, and driver logic for an external power MOSFET (intended to replace a bulky and power-dissipating reverse-current protection diode).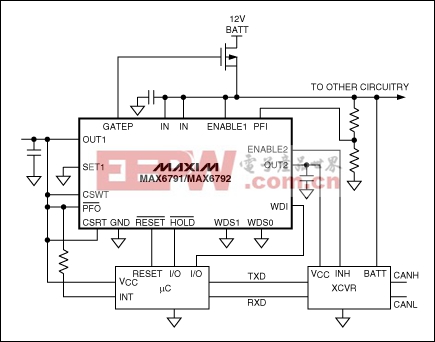
Figure 6. This automotive linear regulator contains two linear regulators plus a set of "housekeeping" functions. It can dissipate 2.7W at 70°C.
模拟电路 模拟芯片 德州仪器 放大器 ADI 模拟电子 相关文章:
- 12位串行A/D转换器MAX187的应用(10-06)
- AGC中频放大器设计(下)(10-07)
- 低功耗、3V工作电压、精度0.05% 的A/D变换器(10-09)
- PIC16C5X单片机睡眠状态的键唤醒方法(11-16)
- 用简化方法对高可用性系统中的电源进行数字化管理(10-02)
- 利用GM6801实现智能快速充电器设计(11-20)
