高侧电流检测的测量:集成电路和原则-High-Side
时间:05-27
来源:互联网
点击:
- large difference in input resistance.
- Resistors must be very well matched to obtain an acceptable common-mode rejection ratio (CMRR): A 0.01% deviation in any resistor value lowers the CMRR to 86dB, a 0.1% deviation lowers it to 66dB, and a 1% deviation lowers it to 46dB.
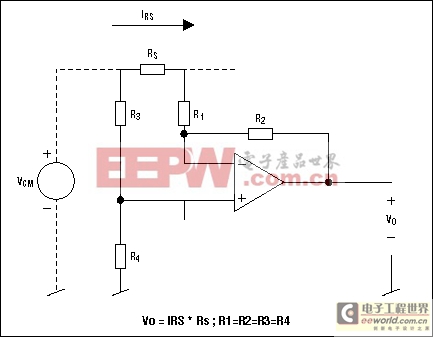
Figure 4. The differential amplifier is a basic component in high-side current measurements.
Integrated Differential Amplifier
The use of differential amplifiers in high-side current measurement recently became more convenient thanks to the introduction of numerous ICs containing not only the precision amplifier but well-matched resistors as well. These devices offer CMRRs on the order of 105dB. An example is the MAX4198/MAX4199 (Figure 5). Available in 8-pin μMAX packages, these ICs achieve a typical CMRR of 110dB and gain error better than 0.01%.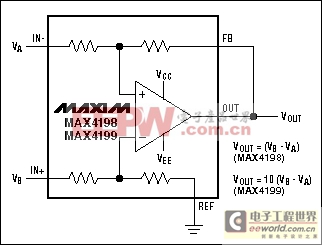
Figure 5. An integrated differential amplifier (MAX4198/MAX4199) exhibits very high CMRR.
Dedicated High-Side Monitors
Another approach to high-side current measurement is represented by ICs that contain all functions necessary to perform the measurement. They sense high-side currents in the presence of common-mode voltages as high as 32V and provide a ground-referenced current- or voltage-source output that is proportional to the current of interest. Power management, battery charging, and other applications that must accurately measure or control current can benefit from these dedicated current-sense amplifiers.High-side current-sense amplifiers from Maxim employ a current-sensing resistor placed between the positive terminal of the power supply and the supply input of the monitored circuit. This arrangement avoids extraneous resistance in the ground plane, greatly simplifies the layout, and generally improves the overall circuit performance. The variety of uni- and bidirectional current-sense ICs from Maxim includes bidirectional devices with or without internal sense resistors. The bidirectional amplifiers comprise a sign pin for indicating current direction.
These uni- and bidirectional current-sense ICs include models with adjustable gain, fixed internal gains of +20V/V, +50V/V, or +100V/V, and internal gain plus a single or dual comparator. They come in small packages to meet the strict demands of compact applications. (Maxim has the only high-side current-sense amplifier in a tiny SOT23 package.)
Common to all high-side IC monitors from Maxim is an ability to provide ground-referenced voltage or current outputs with few or no additional components. The output signal is proportional to the measured high-side current, which can have a common-mode voltage as high as 32V. Figures 6 through 9 show some available architectures for the integrated high-side current monitor. Note that the MAX471/MAX472 current-source output is proportional to the voltage across RSENSE.
Equations for the new high-side monitors indicate that the effect of external resistors on the CMRR is no longer an issue, because CMRR (typically >90dB) is now determined by the integrated amplifier alone. Integration of the current-measure function in a single IC provides the following advantages:
- Tight tolerance on active and passive integrated components
- An excellent temperature coefficient (TC)
- Small size
- Low power consumption
- Ease of use
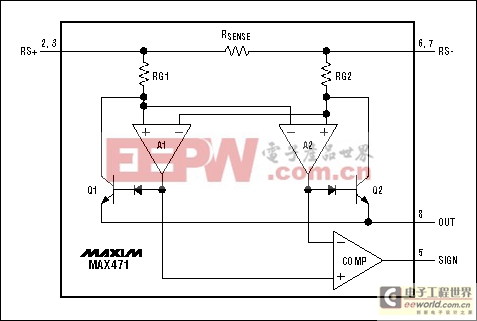
Figure 6. This simplified schematic of a bidirectional high-side current monitor (MAX471/MAX472) includes a SIGN output for current direction.
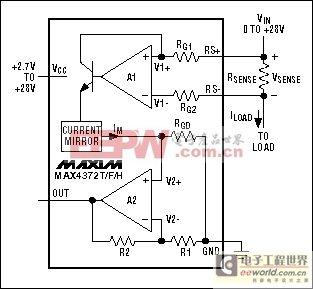
Figure 7. A unidirectional high-side current monitor (MAX4372).
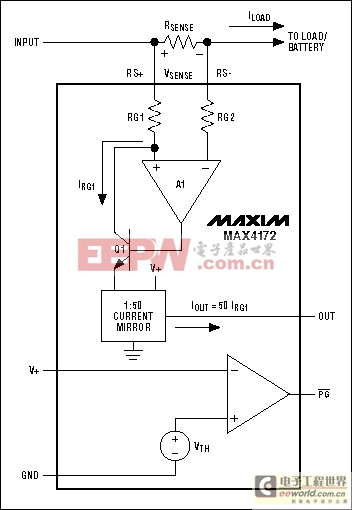
Figure 8. Another unidirectional high-side current monitor (MAX4172).
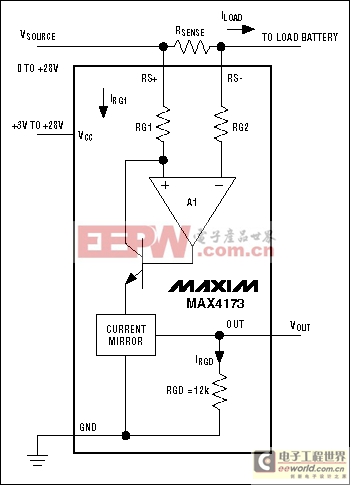
Figure 9. Yet another architecture for the unidirectional high-side current monitor (MAX4173).
Considerations When Selecting RSENSE
A careful consideration of the shunt resistor (RSENSE) is an important and necessary part of designing any kind of current monitor. The following criteria should govern the selection of RSENSE:模拟电源 电源管理 模拟器件 模拟电子 模拟 模拟电路 模拟芯片 德州仪器 放大器 ADI 相关文章:
- 采用数字电源还是模拟电源?(01-17)
- 模拟电源管理与数字电源管理(02-05)
- 数字电源正在超越模拟电源(03-19)
- 数字电源PK模拟电源(04-03)
- TI工程师现身说法:采用数字电源还是模拟电源?(10-10)
- 开关电源与模拟电源的分别(05-08)
