自动白平衡的FPGA实现
时间:07-11
来源:互联网
点击:
摘要:
光源发射光的颜色与黑体在某一温度下辐射光色相同时,黑体的温度称为该光源的色温。在各种不同的色温下,目标物的色彩会产生变化。其中,白色物体变化得最为明显。为了尽可能减少外来光线对目标颜色造成的影响,在不同的色温条件下都能还原出被摄目标本来的色彩,需要进行色彩校正,以达成正确的色彩平衡,也就是达到白平衡。
一、软件介绍
本系统采用了LATTICE的XP系列芯片,所用软件为splever7.0,应用本软件有一个新加功能,可以用FPGA的底层资源生成一个简单CPU的框架,并且在软件的库里边,有很多的模块可以调用,例如GPIO接口,I2C接口等。本系统的设计使用的是I2C接口。
二、系统构成
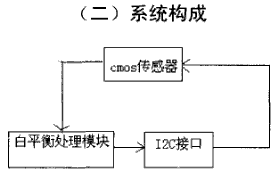
图1 系统框图
本系统(系统框图如图1)是采用FPGA进行实时运算。从cmos传感器出来的数字信号首先经过白平衡处理模块,在这个模块中,需要对图象中的R、G、B的分量分别进行计算,求出他们各自的均值。一般情况下,只有当他们各自的均值为128或者129的时候,我们可以认为图象达到了白平衡的状态,当然有一个前提就是要对一个白色的背景取图。如果他们的均值不相等,或者没有达到128或者129的值时,给I2C模块一个信号,使之对传感器的颜色分量寄存器进行设置,直到完全为我们所期待的数值为止。
三、部分程序和接口
module send( reset_n,
clk,
vsync,
href,
data_in,
data_out);
input reset_n;
//系统复位信号
input clk;
//系统时钟
input vsync;
//厂信号
input href;
//行信号
input [9:0]data_in;
//图象数据
output [29:0]data_out;//色彩分量均值
reg [25:0]count_r;
always@(negedge clk or posedge posevsync)begin
if(posevsync)
count_r <= 26'h00000000;
else begin
if(hs_count>=10'd129&&hs_count<=10'd640)
begin
if((pixcount>=11'd384&&pixcount<=11'd895)&&row_odd_href)
begin
if(!row_odd_pix)
count_r <= count_r + data_in;
else
count_r <= count_r;
end
else
count_r <= count_r;
end
else
count_r <= count_r;
end
end
reg [26:0]count_g;
always@(negedge clk or posedge posevsync)begin
if(posevsync)
count_g <= 27'h00000000;
else begin
if(hs_count>=10'd129&&hs_count<=10'd640)
begin
if(pixcount>=11'd384&&pixcount<=11'd895)
begin
if(row_odd_href)
begin
if(row_odd_pix)
count_g <= count_g + data_in;
else
count_g <= count_g;
end
else begin
if(!row_odd_pix)
count_g <= count_g + data_in;
else
count_g <= count_g;
end
end
else
count_g <= count_g;
end
else
count_g <= count_g;
end
end
reg [25:0]count_b;
always@(negedge clk or posedge posevsync)begin
if(posevsync)
count_b <= 26'h00000000;
else begin
if(hs_count>=10'd129&&hs_count<=10'd640)
begin
if((pixcount>=11'd384&&pixcount<=11'd895)&&(!row_odd_href))
begin
if(row_odd_pix)
count_b <= count_b + data_in;
else
count_b <= count_b;
end
else
count_b <= count_b;
end
else
count_b <= count_b;
end
end
reg [29:0]data_out;
always@(negedge vsync or negedge reset_n)begin
if(!reset_n)
data_out <= 30'h0000000000;
else
data_out
<= {count_r[25:16], count_g[26:17], count_b[25:16]};
end
四、仿真图形
系统的总体仿真图如图2

图2 系统仿真图
五、结论
采用FPGA对自动白平衡进行运算的一个最大的优点就是所有的操作都是实时进行,不需要先缓存一整张图象,所以中间没有延时,不仅运算速度快,而且图像的相质还可以得到很好的改良。
光源发射光的颜色与黑体在某一温度下辐射光色相同时,黑体的温度称为该光源的色温。在各种不同的色温下,目标物的色彩会产生变化。其中,白色物体变化得最为明显。为了尽可能减少外来光线对目标颜色造成的影响,在不同的色温条件下都能还原出被摄目标本来的色彩,需要进行色彩校正,以达成正确的色彩平衡,也就是达到白平衡。
一、软件介绍
本系统采用了LATTICE的XP系列芯片,所用软件为splever7.0,应用本软件有一个新加功能,可以用FPGA的底层资源生成一个简单CPU的框架,并且在软件的库里边,有很多的模块可以调用,例如GPIO接口,I2C接口等。本系统的设计使用的是I2C接口。
二、系统构成

图1 系统框图
本系统(系统框图如图1)是采用FPGA进行实时运算。从cmos传感器出来的数字信号首先经过白平衡处理模块,在这个模块中,需要对图象中的R、G、B的分量分别进行计算,求出他们各自的均值。一般情况下,只有当他们各自的均值为128或者129的时候,我们可以认为图象达到了白平衡的状态,当然有一个前提就是要对一个白色的背景取图。如果他们的均值不相等,或者没有达到128或者129的值时,给I2C模块一个信号,使之对传感器的颜色分量寄存器进行设置,直到完全为我们所期待的数值为止。
三、部分程序和接口
module send( reset_n,
clk,
vsync,
href,
data_in,
data_out);
input reset_n;
//系统复位信号
input clk;
//系统时钟
input vsync;
//厂信号
input href;
//行信号
input [9:0]data_in;
//图象数据
output [29:0]data_out;//色彩分量均值
reg [25:0]count_r;
always@(negedge clk or posedge posevsync)begin
if(posevsync)
count_r <= 26'h00000000;
else begin
if(hs_count>=10'd129&&hs_count<=10'd640)
begin
if((pixcount>=11'd384&&pixcount<=11'd895)&&row_odd_href)
begin
if(!row_odd_pix)
count_r <= count_r + data_in;
else
count_r <= count_r;
end
else
count_r <= count_r;
end
else
count_r <= count_r;
end
end
reg [26:0]count_g;
always@(negedge clk or posedge posevsync)begin
if(posevsync)
count_g <= 27'h00000000;
else begin
if(hs_count>=10'd129&&hs_count<=10'd640)
begin
if(pixcount>=11'd384&&pixcount<=11'd895)
begin
if(row_odd_href)
begin
if(row_odd_pix)
count_g <= count_g + data_in;
else
count_g <= count_g;
end
else begin
if(!row_odd_pix)
count_g <= count_g + data_in;
else
count_g <= count_g;
end
end
else
count_g <= count_g;
end
else
count_g <= count_g;
end
end
reg [25:0]count_b;
always@(negedge clk or posedge posevsync)begin
if(posevsync)
count_b <= 26'h00000000;
else begin
if(hs_count>=10'd129&&hs_count<=10'd640)
begin
if((pixcount>=11'd384&&pixcount<=11'd895)&&(!row_odd_href))
begin
if(row_odd_pix)
count_b <= count_b + data_in;
else
count_b <= count_b;
end
else
count_b <= count_b;
end
else
count_b <= count_b;
end
end
reg [29:0]data_out;
always@(negedge vsync or negedge reset_n)begin
if(!reset_n)
data_out <= 30'h0000000000;
else
data_out
<= {count_r[25:16], count_g[26:17], count_b[25:16]};
end
四、仿真图形
系统的总体仿真图如图2

图2 系统仿真图
五、结论
采用FPGA对自动白平衡进行运算的一个最大的优点就是所有的操作都是实时进行,不需要先缓存一整张图象,所以中间没有延时,不仅运算速度快,而且图像的相质还可以得到很好的改良。
- 基于FPGA的片上系统的无线保密通信终端(02-16)
- 基于Virtex-5 FPGA设计Gbps无线通信基站(05-12)
- 基于FPGA的DVI/HDMI接口实现(05-13)
- 基于ARM的嵌入式系统中从串配置FPGA的实现(06-09)
- 采用EEPROM对大容量FPGA芯片数据实现串行加载(03-18)
- 赛灵思:可编程逻辑不仅已是大势所趋,而且势不可挡(07-24)
