MAX44009环境光传感器LCD背光亮度的控制应用
最后一步就是在传感器和执行器之间建立连接,通过微控制器实现。有人可能首先要问:"环境光强如何映射到背光亮度?"事实上,有些文献专门介绍了相关方案。其中一种映射方式是,Microsoft®针对运行Windows® 7¹操作系统的计算机提出的。图7所示曲线是由Microsoft提供的,它可以将环境光强度映射到显示屏亮度(以全部亮度的百分比表示)。
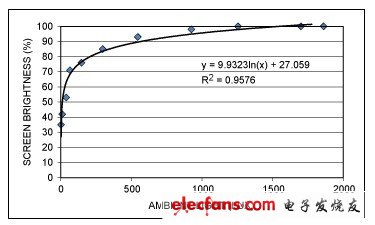
图7. 将环境光强映射为最佳显示屏亮度的曲线示例
这种特殊曲线可以用以下函数表示:
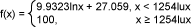
如果设备采用的是已集成亮度控制功能的LCD控制芯片,就可通过向芯片发送指令,轻松设置背光亮度。如果设备采用的是PWM直接控制亮度,则要考虑如何将比例信号映射至显示屏亮度。
在MAX1698示例中,根据其产品说明书的介绍,可以将驱动电流映射为电压。通过这个示例,我们可以假设LED电流强度几乎与其电流呈线性关系。这样,我们就可以在上述等式中乘上一个系数,计算出PWM所映射的有效电压,该电压再被映射至LED电流,最后转化成显示屏亮度。
方案实施
最好不要从一个亮度级直接跳转到另一个亮度级,而是平滑上调和下调背光亮度,确保不同亮度等级之间无缝过渡。为了达到这一目的,最好采用带有固定或不同亮度步长、可逐步调节亮度的定时中断,也可采用带有可控制LED输入电流的PWM值的定时中断,或者是能够发送到显示屏控制器的串行指令的定时中断。图8提供了这种算法的一个示例。
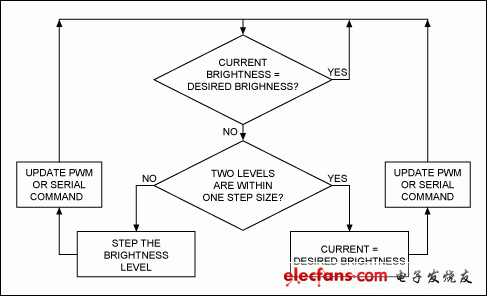
图8. 步进式亮度调节的算法示例
另一个问题是,系统响应环境光强变化的速度。我们应尽量避免过快地改变亮度等级。这是因为光强的瞬间变化(譬如一扇窗户打开或瞬间有一束光扫过)可能导致背光亮度发生不必要的变化,这往往会造成用户感觉不适。并且,较长的响应时间还有助于减少微控制器对光传感器的检测次数,从而可以释放一定的微控制器资源。
最初级的方法就是每隔一两秒钟检查一次光传感器,然后相应地调整背光亮度。更好的方法是,只有光线强度偏离特定范围一定时间后,才对背光亮度进行调节。譬如,如果正常光强是200lux,我们可能只会在光强降到180lux以下或升至220lux以上,而且持续时间超过数秒的情况下才调节亮度。幸运的是,MAX9635和MAX44009都集成了中断引脚和阈值寄存器,可轻松实现这个目的。请参考应用笔记4786"MAX9635环境光传感器的接口程序",获取更多详细信息。
源代码
#define MAX44009_ADDR 0x96
// begin definiTIon of slave addresses for MAX44009
#define INT_STATUS 0x00
#define INT_ENABLE 0x01
#define CONFIG_REG 0x02
#define HIGH_BYTE 0x03
#define LOW_BYTE 0x04
#define THRESH_HIGH 0x05
#define THRESH_LOW 0x06
#define THRESH_TIMER 0x07
// end definiTIon of slave addresses for MAX44009
extern float SCALE_FACTOR; // captures scaling factors to map from % brightness to PWM
float currentBright_pct; // the current screen brightness, in % of maximum
float desiredBright_pct; // the desired screen brightness, in % of maximum
float stepSize; // the step size to use to go from the current
// brightness to the desired brightness
uint8 lightReadingCounter;
/**
* FuncTIon: SetPWMDutyCycle
*
* Arguments: uint16 dc - desired duty cycle
*
* Returns: none
*
* Description: Sets the duty cycle of a 16-bit PWM, assuming that in this
* architecture, 0x0000 = 0% duty cycle
* 0x7FFF = 50% and 0xFFFF = 100%
**/
extern void SetPWMDutyCycle(uint16 dc);
/**
* Function: I2C_WriteByte
*
* Arguments: uint8 slaveAddr - address of the slave device
* uint8 command - destination register in slave device
* uint8 data - data to write to the register
*
* Returns: ACK bit
*
* Description: Performs necessary functions to send one byte of data to a
* specified register in a specific device on the I2C bus
**/
uint8 2C_WriteByte(uint8 slaveAddr, uint8 command, uint8 data);
/**
* Function: I2C_ReadByte
*
* Arguments: uint8 slaveAddr - address of the slave device
* uint8 command - destination register in slave device
* uint8 *data - pointer data to read from the register
*
* Returns: ACK bit
*
* Description: Performs necessary functions to get one byte of data from a
* specified register in a specific device on the I2C bus
**/
uint8 I2C_ReadByte(uint8 slaveAddr, uint8 command, uint8* data);
/**
* Function: getPctBrightFromLuxReading
*
* Arguments: float lux - the pre-computed ambient light level
*
* Returns: The % of maximum brightness to which the backlight should be set
* given the ambient light (0 to 1.0)
*
* Description: Uses a function to map the ambient light level to a backlight
* brightness by using a predetermined function
**/
float getPctBrightFromLuxReading(float lux);
/**
* Function: mapPctBrighttoPWM
*
* Arguments: float pct
*
* Returns: PWM counts needed to achieve the specified % brightness (as
* determined by some scaling factors)
**/
uint16 mapPctBrighttoPWM(float pct);
/**
* Function: getLightLevel
*
* Arguments: n/a
*
* Returns: the ambient light level, in lux
*
* Description: Reads both the light registers on the device and returns the
* computed light level
**/
float getLightLevel(void);
/**
* Function: stepBrightness
*
* Arguments: n/a
*
* Returns: n/a
*
* Description: This function would be called by an interrupt. It looks at the
* current brightness setting, then the desired brightness setting.
* If there is a difference between the two, the current brightness
* setting is stepped closer to its goal.
**/
void stepBrightness(void);
/**
* Function: timerISR
*
* Arguments: n/a
*
* Returns: n/a
*
* Description: An interrupt service routine which fires every 100ms or so. This
* handles all the ambient light sensor and backlight
* control code.
**/
void timerISR(void);
void main() {
SetupMicro(); // some subroutine which initializes this CPU
I2C_WriteByte(MAX44009_ADDR, CONFIG_REG, 0x80); // set to run continuously
lightReadingCounter = 0;
stepSize = .01;
currentBright_pct = 0.5;
desiredBright_pct = 0.5;
SetPWMDutyCycle(mapPctBrighttoPWM(currentBright_pct));
InitializeTimerInterrupt(); // set this to fire every 100ms
while(1) {
// do whatever else you need here, the LCD control is done in interrupts
Idle();
}
} // main routine
// the point at which the function clips to 100%
#define MAXIMUM_LUX_BREAKPOINT 1254.0
float getPctBrightFromLuxReading(float lux) {
if (lux > MAXIMUM_LUX_BREAKPOINT)
return 1.0;
else
return (9.9323*log(x) + 27.059)/100.0;
} // getPctBrightFromLuxReading
uint16 mapPctBrighttoPWM(float pct) {
return (uint16)(0xFFFF * pct * SCALE_FACTOR);
} // mapPctBrighttoPWM
float getLightLevel(void) {
uint8* lowByte;
uint8* highByte;
uint8 exponent;
uint8 mantissa;
float result;
I2C_ReadByte(MAX44009_ADDR, HIGH_BYTE, highByte);
I2C_ReadByte(MAX44009_ADDR, LOW_BYTE, lowByte);
exponent = (highByte & 0xF0) >> 4;// upper four bits of high byte register
mantissa = (highByte & 0x0F) << 4;// lower four bits of high byte register =
// upper four bits of mantissa
mantissa += lowByte & 0x0F; // lower four bits of low byte register =
// lower four bits of mantissa
result = mantissa * (1 << exponent) * 0.045;
return result;
} //getLightLevel
void stepBrightness(void) {
// if current is at desired, don't do anything
if (currentBright_pct == desiredBright_pct)
return;
// is the current brightness above the desired brightness?
else if (currentBright_pct > desiredBright_pct) {
// is the difference between the two less than one step?
if ( (currentBright_pct-stepSize) < desiredBright_pct)
currentBright_pct = desiredBright_pct;
else
currentBright_pct -= stepSize;
} // else if
else if (currentBright_pct < desiredBright_pct) {
// is the difference between the two less than one step?
if ( (currentBright_pct+stepSize) > desiredBright_pct)
currentBright_pct = desiredBright_pct;
else
currentBright_pct += stepSize;
} // else if
SetPWMDutyCycle(mapPctBrighttoPWM(currentBright_pct));
return;
} // stepBrightness
void timerISR(void) {
float lux;
float pctDiff;
stepBrightness();
if (lightReadingCounter)
lightReadingCounter--;
else {
lightReadingCounter = 20; // 2 second delay
lux = getLightLevel();
desiredBright_pct = getPctBrightFromLuxReading(lux);
pctDiff = abs(desiredBright_pct - currentBright_pct);
stepSize = (pctDiff <= 0.01) ? 0.01:pctDiff/10;
} // else
ClearInterruptFlag();
} // timerISR
- 能源有限!智能电网基础解读(09-14)
- MAX9635内置ADC的环境光传感器(02-11)
- MAX44007环境光传感器,改善黑色玻璃的设计性能(03-21)
- 接近传感器为你揭秘:智能手机是否真的智能(06-02)
- 新型高清显示技术优劣对比(11-13)
- 品佳集团推出LCD TV一系列应用解决方案(08-11)
