自制51单片机超大数码管时钟
市面上出售的数码管一般都很小,本人用led发光管自己制作了一种个头很非常大的数码管,挂在家里显示效果非常牛逼下面是实物图:



下面是电路图: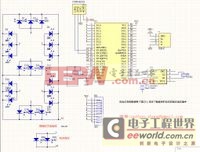
下面是c51程序源代码:
#includereg52.h>
#include intrins.h>
#define uchar unsigned char
#define uint unsigned int
#define pos P0 //设置数码显示的位选
#define segs P1 //设置数码显示的段选
code unsigned char d[]=
{0x3f,0x06,0x5b,0x4f,0x66,0x6d,0x7d,0x07,0x7f,0x6f,0x77,
0x7c,0x39,0x5e,0x79,0x71,0x40,0};
// 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 a b c d e f - 熄灭
//P0段选,共阴数码管 0-9 a-f - 表
unsigned char code w[]={0xfe,0xfd,0xfb,0xf7,0xef,0xdf,0xbf,0x7f};
//P1位选,直接使用P1的8个端口进行8位选择(此演示中未用到)
//ds1302连线设置
sbit SCL2=P2^0; //SCL2定义为P2口的第2位脚,连接DS1302SCL
sbit SDA2=P2^1; //SDA2定义为P2口的第1位脚,连接DS1302SCL
sbit RST = P2^2; // DS1302片选脚
unsigned char now[8]= {0, 19, 9, 17, 1, 7 , 10, 0};
// 秒 分 时 日 月 星期 年 写入禁止(0允许写入,1禁止写入)
unsigned char nowtoshow[8];//进行数据位的拆分处理用
code unsigned char write_rtc_address[7]={0x80,0x82,0x84,0x86,0x88,0x8a,0x8c}; //保存写入寄存器位置
code unsigned char read_rtc_address[7]={0x81,0x83,0x85,0x87,0x89,0x8b,0x8d}; //保存读取寄存器位置
unsigned char flash=0; //闪秒
void display(unsigned char *lp);//数字的显示函数;lp为指向数组的地址,lc为显示的个数
void Write_Ds1302_byte(unsigned char temp); //字节写入函数
void Write_Ds1302( unsigned char address,unsigned char dat ); //调用字节定入函数在特定的地址写入特定的数据
unsigned char Read_Ds1302 ( unsigned char address ); //调用指定的地址的数据
void Read_RTC(void);//read RTC //读取时间日期值到nowtoshow
void Set_RTC(void);//set RTC //设定时间日期值,这里用于赋初值
void keydelay(unsigned char t);////键盘消抖延时
delay();
void main()
{
unsigned int k=0; //使k在0到4000之间循环,不同的时间段显示不同的内容,以较多的时间显示时间,以很少的时间显示日期和星期
//Set_RTC(); //设初值,第一次使用,以后就可以注释掉,以免再次调校时间,当然必须给1302接上2~5.5V的备用电源或电池
Read_RTC();
nowtoshow[0]=now[2]/16; //数据的转换,因我们采用数码管0~9的显示,将数据分开
nowtoshow[1]=now[2]0x0f;
nowtoshow[2]=now[1]/16;
nowtoshow[3]=now[1]0x0f;
display(nowtoshow);
while(1)
{
if (k2000) //显示时间
{
if (k%100==0) //循环1000次后进行一次数据更新
{
Read_RTC();
if (flash==0) //象征性的闪秒,并不准确,也没有必要准确
{ flash=1;}
else
{flash=0;}
nowtoshow[0]=now[2]/16; //数据的转换,因我们采用数码管0~9的显示,将数据分开
if (nowtoshow[0]==0)nowtoshow[0]=17; //如果是0则不显示
nowtoshow[1]=now[2]0x0f;
nowtoshow[2]=now[1]/16;
nowtoshow[3]=now[1]0x0f;
}
}
if (k>2000k2500) //显示日期
{
flash=17;
nowtoshow[0]=now[4]/16; //数据的转换,因我们采用数码管0~9的显示,将数据分开
if (nowtoshow[0]==0)nowtoshow[0]=17; //如果是0则不显示
nowtoshow[1]=now[4]0x0f;
nowtoshow[2]=now[3]/16;
if (nowtoshow[2]==0)nowtoshow[2]=17; //如果是0则不显示
nowtoshow[3]=now[3]0x0f;
}
if (k>2500) //显示星期
{
flash=17;
nowtoshow[0]=17; //数据的转换,因我们采用数码管0~9的显示,将数据分开
nowtoshow[1]=17;
nowtoshow[2]=17;
nowtoshow[3]=now[5];
}
k++;
if (k==3000)k=0;
display(nowtoshow);
}
}
delay()
{
int j;
for (j=0;j100;j++);
}
void display(unsigned char *lp)//显示
{
uint k;
for (k=0;k4;k++)
{
pos=w[k];
segs=d[lp[k]];
delay();
segs=d[17];
}
pos=w[4];
segs=d[flash]; //秒闪烁灯
delay();
segs=d[17];
}
void Write_Ds1302_Byte(unsigned char temp)
{
unsigned char i;
for (i=0;i8;i++) //循环8次 写入数据
{
SCL2=0;
SDA2=temp0x01; //每次传输低字节
temp>>=1; //右移一位
SCL2=1;
}
}
/***********************************************************
*****************/
void Write_Ds1302( unsigned char address,unsigned char dat )
{
RST=0;
_nop_();
SCL2=0;
_nop_();
RST=1;
_nop_(); //启动
Write_Ds1302_Byte(address); //发送地址
Write_Ds1302_Byte(dat); //发送数据
RST=0; //恢复
}
/*********************************************************
- 关于RTX51 TINY的分析与探讨(05-30)
- 浅析8051模块化编程技巧(05-28)
- 基于DSP和单片机通信的液晶显示设计方案(07-20)
- 锁相环控制及初始化简析(08-27)
- 基于MSP430自动胀管控制器的研究(09-07)
- 嵌入式C实现延时程序的不同变量的区别(03-01)
