基于sniffer的网络安全分析仪设计与实现
x,还可以输出数据包的十六进制内容。
6>icmp协议分析
void icmp_printer(u_char *user, const struct pcap_pkthdr *h, const u_char *p)
本函数分析icmp协议,输出icpm协议的源ip地址,目的ip地址,以及类型,比如echo request和echo reply。
-n指定输出的格式,输出域名而不是ip地址。
5)数据包统计
本程序使用SIGINT信号,在键盘上的Ctrl+C快捷键按下后发出终止信号SIGINT,然后程序调用信号处理函数,输出数据包的总大小,捕获时间,还有arp、ip、tcp、udp、icmp、ether网的数据包总个数以及占用的百分比。
signal(SIGINT, sigIntHandler) //用来设定SIGINT信号
void sigIntHandler(int sig) //SIGINT信号处理函数
6)其他辅助函数
char *copy_argv(register char **argv) //BPF内核过滤参数处理
int32_t gmt2local(time_t t) //本地时间转换函数
void ts_print(register const struct timeval *tvp) //时间打印函数
void getportname(int portn,char portch[], char *protocol) //端口号->服务名
static void hex_print(const u_char *buf, int len, int offset)//
十六进制打印
『
struct {
unsigned long int ipaddr;
char hostname[MAXSTRINGSIZE];
}nametable[MAXENTRY]; //ip域名高速缓存
int tbllength=0;
void intohost(unsigned long int iadd, char *hn)
void reghost(unsigned long int iadd)
void print_hostname(u_char *ipadd)
』
arp tool
(1)流程图
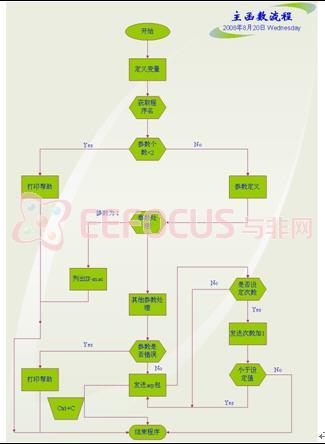
(2)程序明细
★arptool设计
arptool用于扫描局域网的ip、mac地址对应表,并且具有发送arp数据包的功能,可以对付局域网的arp欺骗攻击。
源代码核心函数介绍:
1) 取得本机ip地址
int get_ip(struct in_addr* addr)
本函数使用ioctl系统调用获得系统ip地址,并保存到addr结构体中。
2) 取得子网掩码
int get_mask(struct in_addr* addr)
本函数使用ioctl系统调用获得子网掩码,并保存到addr结构体中。
3) 取得本机硬件地址
int get_packet_sock(struct sockaddr_ll* sll, char *device, u_char hwaddr[])
本函数使用ioctl系统调用获得本机硬件地址,并保存到addr结构体中。
同时可以自己定义硬件地址,用来和arpsend配合。
同时生成一个sockaddr_ll结构体,用来发送arp数据包。
4) 嗅探arp数据包
void* sniff(void* myip)
利用libpcap嗅探数据包,并指定arp数据包,目标地址为本机ip,回调函数为
void handler(u_char* user, const struct pcap_pkthdr* hdr, const u_char* pack)
5) 发送arp数据包
int arpsend_local(int sock, struct sockaddr_ll* sll,u_char* pdip, u_char* pdmac)
int arpsend(int sock, struct sockaddr_ll* sll, u_long SrcIP, u_long DstIP, u_char DstHW[])
arpsend_local为列表ip、mac地址所用的本机arp发包函数。
arpsend是用来发送自定义的arp数据包,供主函数调用。
-n 指定发送的arp包的个数
-a 指定发送arp request包,默认的是arp reply包
-w 指定发送数据包的时间间隔(秒数),默认是1秒
-d 指定发送数据包的目标ip地址
-s 指定发送数据包的源ip地址
-t 指定发送数据包的目标硬件地址
-r 指定发送数据包的源硬件地址
6) 输出ip-mac对应表
int listIPMAC(u_char *device)
本函数里面用新的线程进行监听,线程函数为sniff,同时用arpsend_local发送本机的arp数据包,然后调用下面的函数。
void handler(u_char* user, const struct pcap_pkthdr* hdr, const u_char* pack)
本函数是嗅探arp数据包的回调函数,读取嗅探的arp包,并解析出来源ip和源mac地址,然后输出ip、mac对应表。
3.用户程序建立以及microblaze 上运行
程序板上调试可以使用网络文件系统NFS,但是我的nfs建立不起来,只能使用了另一种方法,因为发现板上uclinux系统有tftp命令,故使用windows系统下的tftp服务器。具体方法如下:
使用petalinux-new-app脚本建立用户程序,并编译。具体方法参考user-apps目录下面的README。
将生成的执行文件通过共享文件夹复制到tftp服务器根目录
目标板上电启动之后,在超级终端,使用ifconfig eth0 x.x.x.x命令分配板上系统一个ip地址。
开启tftp服务器,进入板上系统的可写入目录/var(ramfs文件系统),执行命令
tftp 192.168.158.57(tftp服务器ip) –g –r 可执行文件名
修改可执行文件的权限 chmod 755 可执行文件名
(6)./可执行文件,查看运行结果。
4.软硬件融合
当程序的运行情况符合自己的预期的时候,就可以将其加载到操作系统内核了。具体方法如下:
redhat9系统,在已经建立了petalinux环境的终端中,执行命令进
RevC 网络安全分析仪 libpcap Sniffer程序 局域网简单流量分析 相关文章:
- 基于Zigbee技术家用无线网络的构架(12-14)
- 无线通信领域中的模拟技术发展趋势(蜂窝基站)(09-22)
- 新一代移动通信系统及无线传输关键技术(06-19)
- 蜂窝移动通信基站电磁辐射对人体影响的探讨(04-10)
- 基站升级换代中平衡性能与成本(10-06)
- 在3G与Wi-Fi之间切换 H3C 运营商WLAN解决方案(01-15)
