Linux设备模型分析之kset --转
时间:10-02
整理:3721RD
点击:
Linux设备模型分析之kset
上一篇博客我们分析了linux设备模型中kobject的注册和使用,在这一篇文章中,我们来看一下kset的用法。首先我们看一个使用kset的例子,代码如下:[cpp] view plaincopyprint?
#include <linux/device.h>#include <linux/module.h>#include <linux/kernel.h>#include <linux/init.h>#include <linux/string.h>#include <linux/sysfs.h>#include <linux/stat.h> MODULE_AUTHOR("haoyu");MODULE_LICENSE("Dual BSD/GPL"); struct my_kobject{ int value; struct kobject kobj;}; struct my_kobject my_kobj; void kobject_release(struct kobject *kobject);ssize_t kobject_attr_show(struct kobject *kobject, struct attribute *attr,char *buf);ssize_t kobject_attr_store(struct kobject *kobject,struct attribute *attr,const char *buf, size_t count); struct attribute kobject_attr1 = { .name = "name", .mode = S_IRWXUGO,}; struct attribute kobject_attr2 = { .name = "value", .mode = S_IRWXUGO,}; static struct attribute *kobject_def_attrs[] = { &kobject_attr1, &kobject_attr2, NULL,}; struct sysfs_ops kobject_sysfs_ops ={ .show = kobject_attr_show, .store = kobject_attr_store,}; struct kobj_type ktype ={ .release = kobject_release, .sysfs_ops = &kobject_sysfs_ops, .default_attrs = kobject_def_attrs,}; void kobject_release(struct kobject *kobject){ printk("kobject release.\n");} ssize_t kobject_attr_show(struct kobject *kobject, struct attribute *attr,char *buf){ int count = 0; struct my_kobject *my_kobj = container_of(kobject, struct my_kobject, kobj); printk("kobject attribute show.\n"); if(strcmp(attr->name, "name") == 0) count = sprintf(buf, "%s\n", kobject->name); else if(strcmp(attr->name, "value") == 0) count = sprintf(buf, "%d\n", my_kobj->value); else printk("no this attribute.\n"); return count;} ssize_t kobject_attr_store(struct kobject *kobject,struct attribute *attr,const char *buf, size_t count){ int val; struct my_kobject *my_kobj = container_of(kobject, struct my_kobject, kobj); printk("kobject attribute store.\n"); if(strcmp(attr->name, "name") == 0) printk("Can not change name.\n"); else if(strcmp(attr->name, "value") == 0) { val = buf[0] - '0'; if(val == 0 || val == 1) my_kobj->value = val; else printk("value is '0' or '1'\n"); } else printk("no this attribute.\n"); return count;} int kset_filter(struct kset *kset, struct kobject *kobj){ printk("UEVENT: filter. kobj %s.\n",kobj->name); return 1;} const char *kset_name(struct kset *kset, struct kobject *kobj){ static char buf[20]; printk("UEVENT: name. kobj %s.\n",kobj->name); sprintf(buf,"%s","kset_test"); return buf;} int kset_uevent(struct kset *kset, struct kobject *kobj, struct kobj_uevent_env *env){ int i = 0; printk("UEVENT: uevent. kobj %s.\n",kobj->name); while( i< env->envp_idx){ printk("%s.\n",env->envp); i++; } return 0;} struct kset_uevent_ops uevent_ops ={ .filter = kset_filter, .name = kset_name, .uevent = kset_uevent,}; struct kset *kset_parent;struct kset kset_child; static int kset_test_init(void){ printk("kboject test init.\n"); kset_parent = kset_create_and_add("kset_parent", &uevent_ops, NULL); my_kobj.kobj.kset = kset_parent; kobject_init_and_add(&my_kobj.kobj,&ktype,NULL,"kobject_test"); kobject_set_name(&kset_child.kobj,"kset_child"); kset_child.kobj.kset = kset_parent; kset_register(&kset_child); return 0;} static void kset_test_exit(void){ printk("kobject test exit.\n"); kobject_del(&my_kobj.kobj); kset_unregister(kset_parent); kset_unregister(&kset_child);} module_init(kset_test_init);module_exit(kset_test_exit);
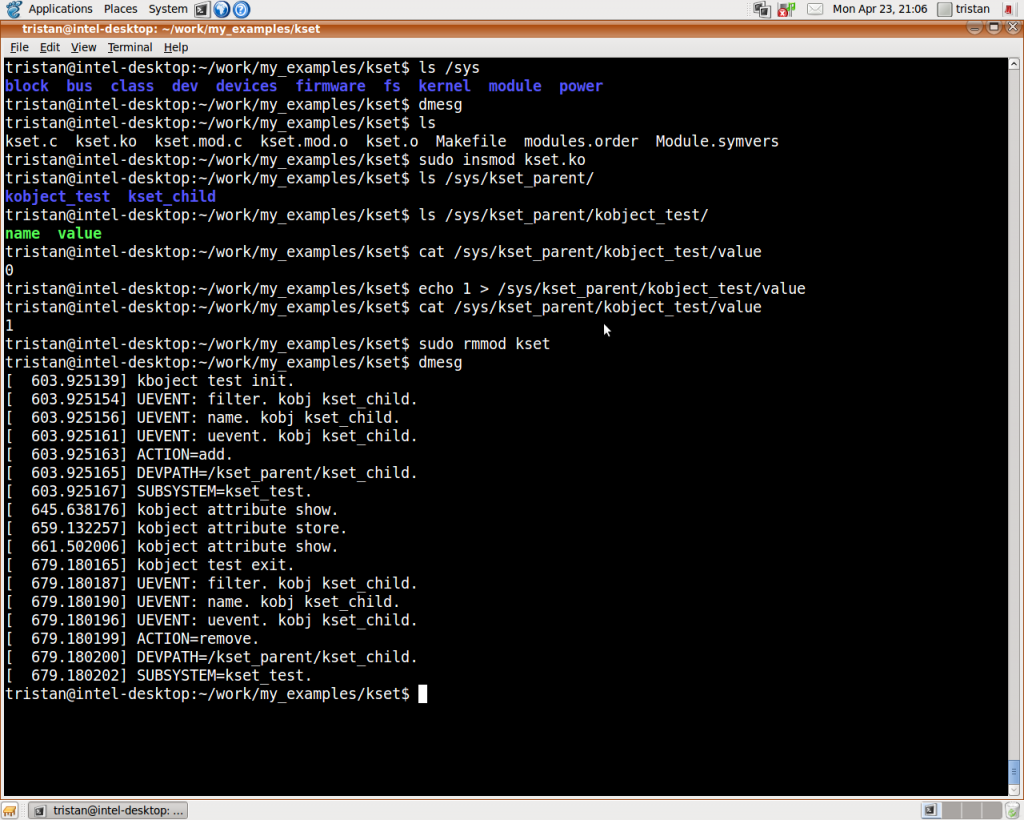
该模块执行结果如下图所示:
 kset的注册使用kset_create_and_add函数,该函数定义如下:[cpp] view plaincopyprint?
kset的注册使用kset_create_and_add函数,该函数定义如下:[cpp] view plaincopyprint?
820/**821 * kset_create_and_add - create a struct kset dynamically and add it to sysfs822 *823 * @name: the name for the kset824 * @uevent_ops: a struct kset_uevent_ops for the kset825 * @parent_kobj: the parent kobject of this kset, if any.826 *827 * This function creates a kset structure dynamically and registers it828 * with sysfs. When you are finished with this structure, call829 * kset_unregister() and the structure will be dynamically freed when it830 * is no longer being used.831 *832 * If the kset was not able to be created, NULL will be returned.833 */834struct kset *kset_create_and_add(const char *name,835 const struct kset_uevent_ops *uevent_ops,836 struct kobject *parent_kobj)837{838 struct kset *kset;839 int error;840841 kset = kset_create(name, uevent_ops, parent_kobj);842 if (!kset)843 return NULL;844 error = kset_register(kset);845 if (error) {846 kfree(kset);847 return NULL;848 }849 return kset;850}
该函数首先调用kset_create创建kset,然后调用kset_register将kset注册到系统中。先来看kset_create函数是如何创建kset的,该函数定义如下:[cpp] view plaincopyprint?
776/**777 * kset_create - create a struct kset dynamically778 *779 * @name: the name for the kset780 * @uevent_ops: a struct kset_uevent_ops for the kset781 * @parent_kobj: the parent kobject of this kset, if any.782 *783 * This function creates a kset structure dynamically. This structure can784 * then be registered with the system and show up in sysfs with a call to785 * kset_register(). When you are finished with this structure, if786 * kset_register() has been called, call kset_unregister() and the787 * structure will be dynamically freed when it is no longer being used.788 *789 * If the kset was not able to be created, NULL will be returned.790 */791static struct kset *kset_create(const char *name,792 const struct kset_uevent_ops *uevent_ops,793 struct kobject *parent_kobj)794{795 struct kset *kset;796 int retval;797798 kset = kzalloc(sizeof(*kset), GFP_KERNEL);799 if (!kset)800 return NULL;801 retval = kobject_set_name(&kset->kobj, name);802 if (retval) {803 kfree(kset);804 return NULL;805 }806 kset->uevent_ops = uevent_ops;807 kset->kobj.parent = parent_kobj;808809 /*810 * The kobject of this kset will have a type of kset_ktype and belong to811 * no kset itself. That way we can properly free it when it is812 * finished being used.813 */814 kset->kobj.ktype = &kset_ktype;815 kset->kobj.kset = NULL;816817 return kset;818}
798行,为kset分配空间。801行,设置kset->kobj的名字,代表该kset的名字。806行,设置kset->uevent_ops。807行,设置kset->kobj.parent。814行,将kset->kobj.ktype设置为&kset_ktype。kset_ktype我们在下面介绍。815行,将kset->kobj.kset设置为NULL,即该kset不属于任何kset。kset_ktype的定义如下:[cpp] view plaincopyprint?
771static struct kobj_type kset_ktype = {772 .sysfs_ops = &kobj_sysfs_ops,773 .release = kset_release,774};
为了分析方便,我们先来看kset_release的定义:[cpp] view plaincopyprint?
763static void kset_release(struct kobject *kobj)764{765 struct kset *kset = container_of(kobj, struct kset, kobj);766 pr_debug("kobject: '%s' (%p): %s\n",767 kobject_name(kobj), kobj, __func__);768 kfree(kset);769}
这个函数取得kset空间指针并释放内存空间。再来看kobj_sysfs_ops的定义,注意其作用,当用户读写kset->kobj的属性文件时,就会调用kset->kobj.ktype.sysfs_ops的show和store函数,即kobj_sysfs_ops的show和store函数:[cpp] view plaincopyprint?
703const struct sysfs_ops kobj_sysfs_ops = {704 .show = kobj_attr_show,705 .store = kobj_attr_store,706};
kobj_attr_show函数定义如下:[cpp] view plaincopyprint?
678/* default kobject attribute operations */679static ssize_t kobj_attr_show(struct kobject *kobj, struct attribute *attr,680 char *buf)681{682 struct kobj_attribute *kattr;683 ssize_t ret = -EIO;684685 kattr = container_of(attr, struct kobj_attribute, attr);686 if (kattr->show)687 ret = kattr->show(kobj, kattr, buf);688 return ret;689}
该函数首先通过container_of宏取得包含指定attribute的kobj_attribute,然后调用kobj_attribute的show函数。kobj_attr_store函数定义如下:[cpp] view plaincopyprint?
691static ssize_t kobj_attr_store(struct kobject *kobj, struct attribute *attr,692 const char *buf, size_t count)693{694 struct kobj_attribute *kattr;695 ssize_t ret = -EIO;696697 kattr = container_of(attr, struct kobj_attribute, attr);698 if (kattr->store)699 ret = kattr->store(kobj, kattr, buf, count);700 return ret;701}
该函数首先通过container_of宏取得包含指定attribute的kobj_attribute,然后调用kobj_attribute的store函数。至此,kset_create函数我们就分析完了,回到kset_create_and_add函数中,下面我们要分析的是kset_register函数,该函数定义如下:[cpp] view plaincopyprint?
708/**709 * kset_register - initialize and add a kset.710 * @k: kset.711 */712int kset_register(struct kset *k)713{714 int err;715716 if (!k)717 return -EINVAL;718719 kset_init(k);720 err = kobject_add_internal(&k->kobj);721 if (err)722 return err;723 kobject_uevent(&k->kobj, KOBJ_ADD);724 return 0;725}
719行,调用kset_init初始化kset。720行,调用kobject_add_internal将kobject注册到系统中,在/sys下建立目录结构和属性文件。该函数我们在前一篇博客<<Linux设备模型之kobject>>已经分析过,这里不再详细分析。723行,调用kobject_uevent函数发送KOBJ_ADD事件。[cpp] view plaincopyprint?
667/**668 * kset_init - initialize a kset for use669 * @k: kset670 */671void kset_init(struct kset *k)672{673 kobject_init_internal(&k->kobj);674 INIT_LIST_HEAD(&k->list);675 spin_lock_init(&k->list_lock);676}
673行,调用kobject_init_internal初始化kset->kobj。这个函数我们在上一篇博客<<Linux设备模型之kobject>>中已经分析过了。kobject_uevent函数定义如下:[cpp] view plaincopyprint?
319/**320 * kobject_uevent - notify userspace by sending an uevent321 *322 * @action: action that is happening323 * @kobj: struct kobject that the action is happening to324 *325 * Returns 0 if kobject_uevent() is completed with success or the326 * corresponding error when it fails.327 */328int kobject_uevent(struct kobject *kobj, enum kobject_action action)329{330 return kobject_uevent_env(kobj, action, NULL);331}
这个函数直接调用了kobject_uevent_env函数,定义如下:[cpp] view plaincopyprint?
119/**120 * kobject_uevent_env - send an uevent with environmental data121 *122 * @action: action that is happening123 * @kobj: struct kobject that the action is happening to124 * @envp_ext: pointer to environmental data125 *126 * Returns 0 if kobject_uevent_env() is completed with success or the127 * corresponding error when it fails.128 */129int kobject_uevent_env(struct kobject *kobj, enum kobject_action action,130 char *envp_ext[])131{132 struct kobj_uevent_env *env;133 const char *action_string = kobject_actions[action];134 const char *devpath = NULL;135 const char *subsystem;136 struct kobject *top_kobj;137 struct kset *kset;138 const struct kset_uevent_ops *uevent_ops;139 u64 seq;140 int i = 0;141 int retval = 0;142#ifdef CONFIG_NET143 struct uevent_sock *ue_sk;144#endif145146 pr_debug("kobject: '%s' (%p): %s\n",147 kobject_name(kobj), kobj, __func__);148149 /* search the kset we belong to */150 top_kobj = kobj;151 while (!top_kobj->kset && top_kobj->parent)152 top_kobj = top_kobj->parent;153154 if (!top_kobj->kset) {155 pr_debug("kobject: '%s' (%p): %s: attempted to send uevent "156 "without kset!\n", kobject_name(kobj), kobj,157 __func__);158 return -EINVAL;159 }160161 kset = top_kobj->kset;162 uevent_ops = kset->uevent_ops;163164 /* skip the event, if uevent_suppress is set*/165 if (kobj->uevent_suppress) {166 pr_debug("kobject: '%s' (%p): %s: uevent_suppress "167 "caused the event to drop!\n",168 kobject_name(kobj), kobj, __func__);169 return 0;170 }171 /* skip the event, if the filter returns zero. */172 if (uevent_ops && uevent_ops->filter)173 if (!uevent_ops->filter(kset, kobj)) {174 pr_debug("kobject: '%s' (%p): %s: filter function "175 "caused the event to drop!\n",176 kobject_name(kobj), kobj, __func__);177 return 0;178 }179180 /* originating subsystem */181 if (uevent_ops && uevent_ops->name)182 subsystem = uevent_ops->name(kset, kobj);183 else184 subsystem = kobject_name(&kset->kobj);185 if (!subsystem) {186 pr_debug("kobject: '%s' (%p): %s: unset subsystem caused the "187 "event to drop!\n", kobject_name(kobj), kobj,188 __func__);189 return 0;190 }191192 /* environment buffer */193 env = kzalloc(sizeof(struct kobj_uevent_env), GFP_KERNEL);194 if (!env)195 return -ENOMEM;196197 /* complete object path */198 devpath = kobject_get_path(kobj, GFP_KERNEL);199 if (!devpath) {200 retval = -ENOENT;201 goto exit;202 }203204 /* default keys */205 retval = add_uevent_var(env, "ACTION=%s", action_string);206 if (retval)207 goto exit;208 retval = add_uevent_var(env, "DEVPATH=%s", devpath);209 if (retval)210 goto exit;211 retval = add_uevent_var(env, "SUBSYSTEM=%s", subsystem);212 if (retval)213 goto exit;214215 /* keys passed in from the caller */216 if (envp_ext) {217 for (i = 0; envp_ext; i++) {218 retval = add_uevent_var(env, "%s", envp_ext);219 if (retval)220 goto exit;221 }222 }223224 /* let the kset specific function add its stuff */225 if (uevent_ops && uevent_ops->uevent) {226 retval = uevent_ops->uevent(kset, kobj, env);227 if (retval) {228 pr_debug("kobject: '%s' (%p): %s: uevent() returned "229 "%d\n", kobject_name(kobj), kobj,230 __func__, retval);231 goto exit;232 }233 }234235 /*236 * Mark "add" and "remove" events in the object to ensure proper237 * events to userspace during automatic cleanup. If the object did238 * send an "add" event, "remove" will automatically generated by239 * the core, if not already done by the caller.240 */241 if (action == KOBJ_ADD)242 kobj->state_add_uevent_sent = 1;243 else if (action == KOBJ_REMOVE)244 kobj->state_remove_uevent_sent = 1;245246 /* we will send an event, so request a new sequence number */247 spin_lock(&sequence_lock);248 seq = ++uevent_seqnum;249 spin_unlock(&sequence_lock);250 retval = add_uevent_var(env, "SEQNUM=%llu", (unsigned long long)seq);251 if (retval)252 goto exit;253254#if defined(CONFIG_NET)255 /* send netlink message */256 mutex_lock(&uevent_sock_mutex);257 list_for_each_entry(ue_sk, &uevent_sock_list, list) {258 struct sock *uevent_sock = ue_sk->sk;259 struct sk_buff *skb;260 size_t len;261262 /* allocate message with the maximum possible size */263 len = strlen(action_string) + strlen(devpath) + 2;264 skb = alloc_skb(len + env->buflen, GFP_KERNEL);265 if (skb) {266 char *scratch;267268 /* add header */269 scratch = skb_put(skb, len);270 sprintf(scratch, "%s@%s", action_string, devpath);271272 /* copy keys to our continuous event payload buffer */273 for (i = 0; i < env->envp_idx; i++) {274 len = strlen(env->envp) + 1;275 scratch = skb_put(skb, len);276 strcpy(scratch, env->envp);277 }278279 NETLINK_CB(skb).dst_group = 1;280 retval = netlink_broadcast_filtered(uevent_sock, skb,281 0, 1, GFP_KERNEL,282 kobj_bcast_filter,283 kobj);284 /* ENOBUFS should be handled in userspace */285 if (retval == -ENOBUFS)286 retval = 0;287 } else288 retval = -ENOMEM;289 }290 mutex_unlock(&uevent_sock_mutex);291#endif292293 /* call uevent_helper, usually only enabled during early boot */294 if (uevent_helper[0] && !kobj_usermode_filter(kobj)) {295 char *argv [3];296297 argv [0] = uevent_helper;298 argv [1] = (char *)subsystem;299 argv [2] = NULL;300 retval = add_uevent_var(env, "HOME=/");301 if (retval)302 goto exit;303 retval = add_uevent_var(env,304 "PATH=/sbin:/bin:/usr/sbin:/usr/bin");305 if (retval)306 goto exit;307308 retval = call_usermodehelper(argv[0], argv,309 env->envp, UMH_WAIT_EXEC);310 }311312exit:313 kfree(devpath);314 kfree(env);315 return retval;316}
133由参数action取得代表事件类型的字符串。kobject_actions定义如下:[cpp] view plaincopyprint?
40/*41 * The actions here must match the index to the string array42 * in lib/kobject_uevent.c43 *44 * Do not add new actions here without checking with the driver-core45 * maintainers. Action strings are not meant to express subsystem46 * or device specific properties. In most cases you want to send a47 * kobject_uevent_env(kobj, KOBJ_CHANGE, env) with additional event48 * specific variables added to the event environment.49 */50enum kobject_action {51 KOBJ_ADD,52 KOBJ_REMOVE,53 KOBJ_CHANGE,54 KOBJ_MOVE,55 KOBJ_ONLINE,56 KOBJ_OFFLINE,57 KOBJ_MAX58};42/* the strings here must match the enum in include/linux/kobject.h */43static const char *kobject_actions[] = {44 [KOBJ_ADD] = "add",45 [KOBJ_REMOVE] = "remove",46 [KOBJ_CHANGE] = "change",47 [KOBJ_MOVE] = "move",48 [KOBJ_ONLINE] = "online",49 [KOBJ_OFFLINE] = "offline",50};
149 - 162行,因为只有kset才包含处理uevent的函数,即kset.uevent_ops,所以这里查找kobj所属的kset,如果kobj->kset不存在,就沿着kobj->parent向上查找,直到找到一个不为空的kset为止。如果确实没有找到kset,则退出。165 - 170行,如果kobj->uevent_suppress的值为1,表示禁止发出uevent事件,退出。172 - 178行,如果uevent_ops不为空,并且实现了uevent_ops->filter,则执行uevent_ops->filter,如果uevent_ops->filter返回值为0,表示这个uevent被过滤了,退出。181 - 190行,如果uevent_ops不为空,并且实现了uevent_ops->name,则通过uevent_ops->name获得子系统名,如果uevent_ops为空,或者没有实现uevent_ops->name,则以kset->kobj的名字作为子系统名。193行,创建kobj_uevent_env结构体变量env,用来保存环境变量。198行,通过调用kobject_get_path函数取得kobj在/sys系统中的路径,保存在devpath变量中。205 - 213行,通过调用add_uevent_var函数将事件名,kobj路径和子系统名加入到环境变量env中。216 - 222行,如果有通过参数传递的环境变量,也调用add_uevent_var函数加入到环境变量env中。225 - 233行,如果uevent_ops不为空,并且实现了uevent_ops->uevent函数,则调用uevent_ops->uevent。241 - 244行,如果要发送的事件是KOBJ_ADD或KOBJ_REMOVE,则相应将kobj->state_add_uevent_sent或kobj->state_remove_uevent_sent置为1。247 - 252行,将发送事件序列数加1,添加到环境变量env中。254 - 291行,条件编译部分我们不分析。294行,先来看uevent_helper的定义:char uevent_helper[UEVENT_HELPER_PATH_LEN] = CONFIG_UEVENT_HELPER_PATH;#define UEVENT_HELPER_PATH_LEN 256CONFIG_UEVENT_HELPER_PATH="/sbin/hotplug"所以uevent_helper就是"/sbin/hotplug"。300 - 306行,将HOME和PATH加入环境变量env中。308 - 309行,执行用户空间的/sbin/hotplug程序,传递环境变量为env。至此, kobject_uevent_env -> kobject_uevent -> kset_register -> kset_create_and_add函数就分析完了,kset被创建和注册到系统中。
上一篇博客我们分析了linux设备模型中kobject的注册和使用,在这一篇文章中,我们来看一下kset的用法。首先我们看一个使用kset的例子,代码如下:[cpp] view plaincopyprint?
- #include <linux/module.h>
#include <linux/kernel.h> - #include <linux/init.h>
#include <linux/string.h> - #include <linux/sysfs.h>
#include <linux/stat.h> -
MODULE_AUTHOR("haoyu"); - MODULE_LICENSE("Dual BSD/GPL");
- struct my_kobject
{ - int value;
struct kobject kobj; - };
- struct my_kobject my_kobj;
- void kobject_release(struct kobject *kobject);
ssize_t kobject_attr_show(struct kobject *kobject, struct attribute *attr,char *buf); - ssize_t kobject_attr_store(struct kobject *kobject,struct attribute *attr,const char *buf, size_t count);
- struct attribute kobject_attr1 = {
.name = "name", - .mode = S_IRWXUGO,
}; -
struct attribute kobject_attr2 = { - .name = "value",
.mode = S_IRWXUGO, - };
- static struct attribute *kobject_def_attrs[] = {
&kobject_attr1, - &kobject_attr2,
NULL, - };
- struct sysfs_ops kobject_sysfs_ops =
{ - .show = kobject_attr_show,
.store = kobject_attr_store, - };
- struct kobj_type ktype =
{ - .release = kobject_release,
.sysfs_ops = &kobject_sysfs_ops, - .default_attrs = kobject_def_attrs,
}; -
void kobject_release(struct kobject *kobject) - {
printk("kobject release.\n"); - }
- ssize_t kobject_attr_show(struct kobject *kobject, struct attribute *attr,char *buf)
{ - int count = 0;
struct my_kobject *my_kobj = container_of(kobject, struct my_kobject, kobj); - printk("kobject attribute show.\n");
if(strcmp(attr->name, "name") == 0) - count = sprintf(buf, "%s\n", kobject->name);
else if(strcmp(attr->name, "value") == 0) - count = sprintf(buf, "%d\n", my_kobj->value);
else - printk("no this attribute.\n");
- return count;
} -
ssize_t kobject_attr_store(struct kobject *kobject,struct attribute *attr,const char *buf, size_t count) - {
int val; - struct my_kobject *my_kobj = container_of(kobject, struct my_kobject, kobj);
printk("kobject attribute store.\n"); - if(strcmp(attr->name, "name") == 0)
printk("Can not change name.\n"); - else if(strcmp(attr->name, "value") == 0)
{ - val = buf[0] - '0';
if(val == 0 || val == 1) - my_kobj->value = val;
else - printk("value is '0' or '1'\n");
} - else
printk("no this attribute.\n"); -
return count; - }
- int kset_fiLTEr(struct kset *kset, struct kobject *kobj)
{ - printk("UEVENT: filter. kobj %s.\n",kobj->name);
return 1; - }
- const char *kset_name(struct kset *kset, struct kobject *kobj)
{ - static char buf[20];
printk("UEVENT: name. kobj %s.\n",kobj->name); - sprintf(buf,"%s","kset_test");
return buf; - }
- int kset_uevent(struct kset *kset, struct kobject *kobj,
struct kobj_uevent_env *env) - {
int i = 0; - printk("UEVENT: uevent. kobj %s.\n",kobj->name);
- while( i< env->envp_idx){
printk("%s.\n",env->envp);- i++;
}
return 0;- }
- struct kset_uevent_ops uevent_ops =
{- .filter = kset_filter,
.name = kset_name,- .uevent = kset_uevent,
};
struct kset *kset_parent;- struct kset kset_child;
- static int kset_test_init(void)
{- printk("kboject test init.\n");
kset_parent = kset_create_and_add("kset_parent", &uevent_ops, NULL);- my_kobj.kobj.kset = kset_parent;
kobject_init_and_add(&my_kobj.kobj,&ktype,NULL,"kobject_test");
kobject_set_name(&kset_child.kobj,"kset_child");- kset_child.kobj.kset = kset_parent;
kset_register(&kset_child);
return 0;- }
- static void kset_test_exit(void)
{- printk("kobject test exit.\n");
kobject_del(&my_kobj.kobj);- kset_unregister(kset_parent);
kset_unregister(&kset_child);- }
- module_init(kset_test_init);
- module_exit(kset_test_exit);
- i++;
#include <linux/device.h>
#include <linux/device.h>#include <linux/module.h>#include <linux/kernel.h>#include <linux/init.h>#include <linux/string.h>#include <linux/sysfs.h>#include <linux/stat.h> MODULE_AUTHOR("haoyu");MODULE_LICENSE("Dual BSD/GPL"); struct my_kobject{ int value; struct kobject kobj;}; struct my_kobject my_kobj; void kobject_release(struct kobject *kobject);ssize_t kobject_attr_show(struct kobject *kobject, struct attribute *attr,char *buf);ssize_t kobject_attr_store(struct kobject *kobject,struct attribute *attr,const char *buf, size_t count); struct attribute kobject_attr1 = { .name = "name", .mode = S_IRWXUGO,}; struct attribute kobject_attr2 = { .name = "value", .mode = S_IRWXUGO,}; static struct attribute *kobject_def_attrs[] = { &kobject_attr1, &kobject_attr2, NULL,}; struct sysfs_ops kobject_sysfs_ops ={ .show = kobject_attr_show, .store = kobject_attr_store,}; struct kobj_type ktype ={ .release = kobject_release, .sysfs_ops = &kobject_sysfs_ops, .default_attrs = kobject_def_attrs,}; void kobject_release(struct kobject *kobject){ printk("kobject release.\n");} ssize_t kobject_attr_show(struct kobject *kobject, struct attribute *attr,char *buf){ int count = 0; struct my_kobject *my_kobj = container_of(kobject, struct my_kobject, kobj); printk("kobject attribute show.\n"); if(strcmp(attr->name, "name") == 0) count = sprintf(buf, "%s\n", kobject->name); else if(strcmp(attr->name, "value") == 0) count = sprintf(buf, "%d\n", my_kobj->value); else printk("no this attribute.\n"); return count;} ssize_t kobject_attr_store(struct kobject *kobject,struct attribute *attr,const char *buf, size_t count){ int val; struct my_kobject *my_kobj = container_of(kobject, struct my_kobject, kobj); printk("kobject attribute store.\n"); if(strcmp(attr->name, "name") == 0) printk("Can not change name.\n"); else if(strcmp(attr->name, "value") == 0) { val = buf[0] - '0'; if(val == 0 || val == 1) my_kobj->value = val; else printk("value is '0' or '1'\n"); } else printk("no this attribute.\n"); return count;} int kset_filter(struct kset *kset, struct kobject *kobj){ printk("UEVENT: filter. kobj %s.\n",kobj->name); return 1;} const char *kset_name(struct kset *kset, struct kobject *kobj){ static char buf[20]; printk("UEVENT: name. kobj %s.\n",kobj->name); sprintf(buf,"%s","kset_test"); return buf;} int kset_uevent(struct kset *kset, struct kobject *kobj, struct kobj_uevent_env *env){ int i = 0; printk("UEVENT: uevent. kobj %s.\n",kobj->name); while( i< env->envp_idx){ printk("%s.\n",env->envp); i++; } return 0;} struct kset_uevent_ops uevent_ops ={ .filter = kset_filter, .name = kset_name, .uevent = kset_uevent,}; struct kset *kset_parent;struct kset kset_child; static int kset_test_init(void){ printk("kboject test init.\n"); kset_parent = kset_create_and_add("kset_parent", &uevent_ops, NULL); my_kobj.kobj.kset = kset_parent; kobject_init_and_add(&my_kobj.kobj,&ktype,NULL,"kobject_test"); kobject_set_name(&kset_child.kobj,"kset_child"); kset_child.kobj.kset = kset_parent; kset_register(&kset_child); return 0;} static void kset_test_exit(void){ printk("kobject test exit.\n"); kobject_del(&my_kobj.kobj); kset_unregister(kset_parent); kset_unregister(&kset_child);} module_init(kset_test_init);module_exit(kset_test_exit);
该模块执行结果如下图所示:
 kset的注册使用kset_create_and_add函数,该函数定义如下:[cpp] view plaincopyprint?
kset的注册使用kset_create_and_add函数,该函数定义如下:[cpp] view plaincopyprint?- 821 * kset_create_and_add - create a struct kset dynaMICally and add it to sysfs
822 * - 823 * @name: the name for the kset
824 * @uevent_ops: a struct kset_uevent_ops for the kset - 825 * @parent_kobj: the parent kobject of this kset, if any.
826 * - 827 * This function creates a kset structure dynamically and registers it
828 * with sysfs. When you are finished with this structure, call - 829 * kset_unregister() and the structure will be dynamically freed when it
830 * is no longer being used. - 831 *
832 * If the kset was not able to be created, NULL will be returned. - 833 */
834struct kset *kset_create_and_add(const char *name, - 835 const struct kset_uevent_ops *uevent_ops,
836 struct kobject *parent_kobj) - 837{
838 struct kset *kset; - 839 int error;
840 - 841 kset = kset_create(name, uevent_ops, parent_kobj);
842 if (!kset) - 843 return NULL;
844 error = kset_register(kset); - 845 if (error) {
846 kfree(kset); - 847 return NULL;
848 } - 849 return kset;
- 850}
820/**
820/**821 * kset_create_and_add - create a struct kset dynamically and add it to sysfs822 *823 * @name: the name for the kset824 * @uevent_ops: a struct kset_uevent_ops for the kset825 * @parent_kobj: the parent kobject of this kset, if any.826 *827 * This function creates a kset structure dynamically and registers it828 * with sysfs. When you are finished with this structure, call829 * kset_unregister() and the structure will be dynamically freed when it830 * is no longer being used.831 *832 * If the kset was not able to be created, NULL will be returned.833 */834struct kset *kset_create_and_add(const char *name,835 const struct kset_uevent_ops *uevent_ops,836 struct kobject *parent_kobj)837{838 struct kset *kset;839 int error;840841 kset = kset_create(name, uevent_ops, parent_kobj);842 if (!kset)843 return NULL;844 error = kset_register(kset);845 if (error) {846 kfree(kset);847 return NULL;848 }849 return kset;850}
该函数首先调用kset_create创建kset,然后调用kset_register将kset注册到系统中。先来看kset_create函数是如何创建kset的,该函数定义如下:[cpp] view plaincopyprint?
- 777 * kset_create - create a struct kset dynamically
778 * - 779 * @name: the name for the kset
780 * @uevent_ops: a struct kset_uevent_ops for the kset - 781 * @parent_kobj: the parent kobject of this kset, if any.
782 * - 783 * This function creates a kset structure dynamically. This structure can
784 * then be registered with the system and show up in sysfs with a call to - 785 * kset_register(). When you are finished with this structure, if
786 * kset_register() has been called, call kset_unregister() and the - 787 * structure will be dynamically freed when it is no longer being used.
788 * - 789 * If the kset was not able to be created, NULL will be returned.
790 */ - 791static struct kset *kset_create(const char *name,
792 const struct kset_uevent_ops *uevent_ops, - 793 struct kobject *parent_kobj)
794{ - 795 struct kset *kset;
796 int retval; - 797
798 kset = kzalloc(sizeof(*kset), GFP_KERNEL); - 799 if (!kset)
800 return NULL; - 801 retval = kobject_set_name(&kset->kobj, name);
802 if (retval) { - 803 kfree(kset);
804 return NULL; - 805 }
806 kset->uevent_ops = uevent_ops; - 807 kset->kobj.parent = parent_kobj;
808 - 809 /*
810 * The kobject of this kset will have a type of kset_ktype and belong to - 811 * no kset itself. That way we can properly free it when it is
812 * finished being used. - 813 */
814 kset->kobj.ktype = &kset_ktype; - 815 kset->kobj.kset = NULL;
816 - 817 return kset;
- 818}
776/**
776/**777 * kset_create - create a struct kset dynamically778 *779 * @name: the name for the kset780 * @uevent_ops: a struct kset_uevent_ops for the kset781 * @parent_kobj: the parent kobject of this kset, if any.782 *783 * This function creates a kset structure dynamically. This structure can784 * then be registered with the system and show up in sysfs with a call to785 * kset_register(). When you are finished with this structure, if786 * kset_register() has been called, call kset_unregister() and the787 * structure will be dynamically freed when it is no longer being used.788 *789 * If the kset was not able to be created, NULL will be returned.790 */791static struct kset *kset_create(const char *name,792 const struct kset_uevent_ops *uevent_ops,793 struct kobject *parent_kobj)794{795 struct kset *kset;796 int retval;797798 kset = kzalloc(sizeof(*kset), GFP_KERNEL);799 if (!kset)800 return NULL;801 retval = kobject_set_name(&kset->kobj, name);802 if (retval) {803 kfree(kset);804 return NULL;805 }806 kset->uevent_ops = uevent_ops;807 kset->kobj.parent = parent_kobj;808809 /*810 * The kobject of this kset will have a type of kset_ktype and belong to811 * no kset itself. That way we can properly free it when it is812 * finished being used.813 */814 kset->kobj.ktype = &kset_ktype;815 kset->kobj.kset = NULL;816817 return kset;818}
798行,为kset分配空间。801行,设置kset->kobj的名字,代表该kset的名字。806行,设置kset->uevent_ops。807行,设置kset->kobj.parent。814行,将kset->kobj.ktype设置为&kset_ktype。kset_ktype我们在下面介绍。815行,将kset->kobj.kset设置为NULL,即该kset不属于任何kset。kset_ktype的定义如下:[cpp] view plaincopyprint?
- 772 .sysfs_ops = &kobj_sysfs_ops,
773 .release = kset_release, - 774};
771static struct kobj_type kset_ktype = {
771static struct kobj_type kset_ktype = {772 .sysfs_ops = &kobj_sysfs_ops,773 .release = kset_release,774};
为了分析方便,我们先来看kset_release的定义:[cpp] view plaincopyprint?
- 764{
765 struct kset *kset = container_of(kobj, struct kset, kobj); - 766 pr_debug("kobject: '%s' (%p): %s\n",
767 kobject_name(kobj), kobj, __func__); - 768 kfree(kset);
- 769}
763static void kset_release(struct kobject *kobj)
763static void kset_release(struct kobject *kobj)764{765 struct kset *kset = container_of(kobj, struct kset, kobj);766 pr_debug("kobject: '%s' (%p): %s\n",767 kobject_name(kobj), kobj, __func__);768 kfree(kset);769}
这个函数取得kset空间指针并释放内存空间。再来看kobj_sysfs_ops的定义,注意其作用,当用户读写kset->kobj的属性文件时,就会调用kset->kobj.ktype.sysfs_ops的show和store函数,即kobj_sysfs_ops的show和store函数:[cpp] view plaincopyprint?
- 704 .show = kobj_attr_show,
705 .store = kobj_attr_store, - 706};
703const struct sysfs_ops kobj_sysfs_ops = {
703const struct sysfs_ops kobj_sysfs_ops = {704 .show = kobj_attr_show,705 .store = kobj_attr_store,706};
kobj_attr_show函数定义如下:[cpp] view plaincopyprint?
- 679static ssize_t kobj_attr_show(struct kobject *kobj, struct attribute *attr,
680 char *buf) - 681{
682 struct kobj_attribute *kattr; - 683 ssize_t ret = -EIO;
684 - 685 kattr = container_of(attr, struct kobj_attribute, attr);
686 if (kattr->show) - 687 ret = kattr->show(kobj, kattr, buf);
688 return ret; - 689}
678/* default kobject attribute operations */
678/* default kobject attribute operations */679static ssize_t kobj_attr_show(struct kobject *kobj, struct attribute *attr,680 char *buf)681{682 struct kobj_attribute *kattr;683 ssize_t ret = -EIO;684685 kattr = container_of(attr, struct kobj_attribute, attr);686 if (kattr->show)687 ret = kattr->show(kobj, kattr, buf);688 return ret;689}
该函数首先通过container_of宏取得包含指定attribute的kobj_attribute,然后调用kobj_attribute的show函数。kobj_attr_store函数定义如下:[cpp] view plaincopyprint?
- 692 const char *buf, size_t count)
693{ - 694 struct kobj_attribute *kattr;
695 ssize_t ret = -EIO; - 696
697 kattr = container_of(attr, struct kobj_attribute, attr); - 698 if (kattr->store)
699 ret = kattr->store(kobj, kattr, buf, count); - 700 return ret;
- 701}
691static ssize_t kobj_attr_store(struct kobject *kobj, struct attribute *attr,
691static ssize_t kobj_attr_store(struct kobject *kobj, struct attribute *attr,692 const char *buf, size_t count)693{694 struct kobj_attribute *kattr;695 ssize_t ret = -EIO;696697 kattr = container_of(attr, struct kobj_attribute, attr);698 if (kattr->store)699 ret = kattr->store(kobj, kattr, buf, count);700 return ret;701}
该函数首先通过container_of宏取得包含指定attribute的kobj_attribute,然后调用kobj_attribute的store函数。至此,kset_create函数我们就分析完了,回到kset_create_and_add函数中,下面我们要分析的是kset_register函数,该函数定义如下:[cpp] view plaincopyprint?
- 709 * kset_register - initialize and add a kset.
710 * @k: kset. - 711 */
712int kset_register(struct kset *k) - 713{
714 int err; - 715
716 if (!k) - 717 return -EINVAL;
718 - 719 kset_init(k);
720 err = kobject_add_internal(&k->kobj); - 721 if (err)
722 return err; - 723 kobject_uevent(&k->kobj, KOBJ_ADD);
724 return 0; - 725}
708/**
708/**709 * kset_register - initialize and add a kset.710 * @k: kset.711 */712int kset_register(struct kset *k)713{714 int err;715716 if (!k)717 return -EINVAL;718719 kset_init(k);720 err = kobject_add_internal(&k->kobj);721 if (err)722 return err;723 kobject_uevent(&k->kobj, KOBJ_ADD);724 return 0;725}
719行,调用kset_init初始化kset。720行,调用kobject_add_internal将kobject注册到系统中,在/sys下建立目录结构和属性文件。该函数我们在前一篇博客<<Linux设备模型之kobject>>已经分析过,这里不再详细分析。723行,调用kobject_uevent函数发送KOBJ_ADD事件。[cpp] view plaincopyprint?
- 668 * kset_init - initialize a kset for use
669 * @k: kset - 670 */
671void kset_init(struct kset *k) - 672{
673 kobject_init_internal(&k->kobj); - 674 INIT_LIST_HEAD(&k->list);
675 SPIn_lock_init(&k->list_lock); - 676}
667/**
667/**668 * kset_init - initialize a kset for use669 * @k: kset670 */671void kset_init(struct kset *k)672{673 kobject_init_internal(&k->kobj);674 INIT_LIST_HEAD(&k->list);675 spin_lock_init(&k->list_lock);676}
673行,调用kobject_init_internal初始化kset->kobj。这个函数我们在上一篇博客<<Linux设备模型之kobject>>中已经分析过了。kobject_uevent函数定义如下:[cpp] view plaincopyprint?
- 320 * kobject_uevent - notify userspace by sending an uevent
321 * - 322 * @action: action that is happening
323 * @kobj: struct kobject that the action is happening to - 324 *
325 * Returns 0 if kobject_uevent() is completed with success or the - 326 * corresponding error when it fails.
327 */ - 328int kobject_uevent(struct kobject *kobj, enum kobject_action action)
329{ - 330 return kobject_uevent_env(kobj, action, NULL);
- 331}
319/**
319/**320 * kobject_uevent - notify userspace by sending an uevent321 *322 * @action: action that is happening323 * @kobj: struct kobject that the action is happening to324 *325 * Returns 0 if kobject_uevent() is completed with success or the326 * corresponding error when it fails.327 */328int kobject_uevent(struct kobject *kobj, enum kobject_action action)329{330 return kobject_uevent_env(kobj, action, NULL);331}
这个函数直接调用了kobject_uevent_env函数,定义如下:[cpp] view plaincopyprint?
- 120 * kobject_uevent_env - send an uevent with environmental data
121 * - 122 * @action: action that is happening
123 * @kobj: struct kobject that the action is happening to - 124 * @envp_ext: pointer to environmental data
125 * - 126 * Returns 0 if kobject_uevent_env() is completed with success or the
127 * corresponding error when it fails. - 128 */
129int kobject_uevent_env(struct kobject *kobj, enum kobject_action action, - 130 char *envp_ext[])
131{ - 132 struct kobj_uevent_env *env;
133 const char *action_string = kobject_actions[action]; - 134 const char *devpath = NULL;
135 const char *subsystem; - 136 struct kobject *top_kobj;
137 struct kset *kset; - 138 const struct kset_uevent_ops *uevent_ops;
139 u64 seq; - 140 int i = 0;
141 int retval = 0; - 142#ifdef CONFIG_NET
143 struct uevent_sock *ue_sk; - 144#endif
145 - 146 pr_debug("kobject: '%s' (%p): %s\n",
147 kobject_name(kobj), kobj, __func__); - 148
149 /* search the kset we belong to */ - 150 top_kobj = kobj;
151 while (!top_kobj->kset && top_kobj->parent) - 152 top_kobj = top_kobj->parent;
153 - 154 if (!top_kobj->kset) {
155 pr_debug("kobject: '%s' (%p): %s: attempted to send uevent " - 156 "without kset!\n", kobject_name(kobj), kobj,
157 __func__); - 158 return -EINVAL;
159 } - 160
161 kset = top_kobj->kset; - 162 uevent_ops = kset->uevent_ops;
163 - 164 /* skip the event, if uevent_suppress is set*/
165 if (kobj->uevent_suppress) { - 166 pr_debug("kobject: '%s' (%p): %s: uevent_suppress "
167 "caused the event to drop!\n", - 168 kobject_name(kobj), kobj, __func__);
169 return 0; - 170 }
171 /* skip the event, if the filter returns zero. */ - 172 if (uevent_ops && uevent_ops->filter)
173 if (!uevent_ops->filter(kset, kobj)) { - 174 pr_debug("kobject: '%s' (%p): %s: filter function "
175 "caused the event to drop!\n", - 176 kobject_name(kobj), kobj, __func__);
177 return 0; - 178 }
179 - 180 /* originating subsystem */
181 if (uevent_ops && uevent_ops->name) - 182 subsystem = uevent_ops->name(kset, kobj);
183 else - 184 subsystem = kobject_name(&kset->kobj);
185 if (!subsystem) { - 186 pr_debug("kobject: '%s' (%p): %s: unset subsystem caused the "
187 "event to drop!\n", kobject_name(kobj), kobj, - 188 __func__);
189 return 0; - 190 }
191 - 192 /* environment buffer */
193 env = kzalloc(sizeof(struct kobj_uevent_env), GFP_KERNEL); - 194 if (!env)
195 return -ENOMEM; - 196
197 /* complete object path */ - 198 devpath = kobject_get_path(kobj, GFP_KERNEL);
199 if (!devpath) { - 200 retval = -ENOENT;
201 goto exit; - 202 }
203 - 204 /* default keys */
205 retval = add_uevent_var(env, "ACTION=%s", action_string); - 206 if (retval)
207 goto exit; - 208 retval = add_uevent_var(env, "DEVPATH=%s", devpath);
209 if (retval) - 210 goto exit;
211 retval = add_uevent_var(env, "SUBSYSTEM=%s", subsystem); - 212 if (retval)
213 goto exit; - 214
215 /* keys passed in fROM the caller */ - 216 if (envp_ext) {
217 for (i = 0; envp_ext; i++) {- 218 retval = add_uevent_var(env, "%s", envp_ext);
219 if (retval)- 220 goto exit;
221 }- 222 }
223- 224 /* let the kset specific function add its stuff */
225 if (uevent_ops && uevent_ops->uevent) {- 226 retval = uevent_ops->uevent(kset, kobj, env);
227 if (retval) {- 228 pr_debug("kobject: '%s' (%p): %s: uevent() returned "
229 "%d\n", kobject_name(kobj), kobj,- 230 __func__, retval);
231 goto exit;- 232 }
233 }- 234
235 /*- 236 * Mark "add" and "remove" events in the object to ensure proper
237 * events to userspace during automatic cleanup. If the object did- 238 * send an "add" event, "remove" will automatically generated by
239 * the core, if not already done by the caller.- 240 */
241 if (action == KOBJ_ADD)- 242 kobj->state_add_uevent_sent = 1;
243 else if (action == KOBJ_REMOVE)- 244 kobj->state_remove_uevent_sent = 1;
245- 246 /* we will send an event, so request a new sequence number */
247 spin_lock(&sequence_lock);- 248 seq = ++uevent_seqnum;
249 spin_unlock(&sequence_lock);- 250 retval = add_uevent_var(env, "SEQNUM=%llu", (unsigned long long)seq);
251 if (retval)- 252 goto exit;
253- 254#if defined(CONFIG_NET)
255 /* send netlink message */- 256 mutex_lock(&uevent_sock_mutex);
257 list_for_each_entry(ue_sk, &uevent_sock_list, list) {- 258 struct sock *uevent_sock = ue_sk->sk;
259 struct sk_buff *skb;- 260 size_t len;
261- 262 /* allocate message with the maximum possible size */
263 len = strlen(action_string) + strlen(devpath) + 2;- 264 skb = alloc_skb(len + env->buflen, GFP_KERNEL);
265 if (skb) {- 266 char *scratch;
267- 268 /* add header */
269 scratch = skb_put(skb, len);- 270 sprintf(scratch, "%s@%s", action_string, devpath);
271- 272 /* copy keys to our continuous event payload buffer */
273 for (i = 0; i < env->envp_idx; i++) {- 274 len = strlen(env->envp) + 1;
275 scratch = skb_put(skb, len);- 276 strcpy(scratch, env->envp);
277 }- 278
279 NETLINK_CB(skb).dst_group = 1;- 280 retval = netlink_broADCast_filtered(uevent_sock, skb,
281 0, 1, GFP_KERNEL,- 282 kobj_bcast_filter,
283 kobj);- 284 /* ENOBUFS should be handled in userspace */
285 if (retval == -ENOBUFS)- 286 retval = 0;
287 } else- 288 retval = -ENOMEM;
289 }- 290 mutex_unlock(&uevent_sock_mutex);
291#endif- 292
293 /* call uevent_helper, usually only enabled during early boot */- 294 if (uevent_helper[0] && !kobj_usermode_filter(kobj)) {
295 char *argv [3];- 296
297 argv [0] = uevent_helper;- 298 argv [1] = (char *)subsystem;
299 argv [2] = NULL;- 300 retval = add_uevent_var(env, "HOME=/");
301 if (retval)- 302 goto exit;
303 retval = add_uevent_var(env,- 304 "PATH=/sbin:/bin:/usr/sbin:/usr/bin");
305 if (retval)- 306 goto exit;
307- 308 retval = call_usermodehelper(argv[0], argv,
309 env->envp, UMH_WAIT_EXEC);- 310 }
311- 312exit:
313 kfree(devpath);- 314 kfree(env);
315 return retval;- 316}
- 218 retval = add_uevent_var(env, "%s", envp_ext);
119/**
119/**120 * kobject_uevent_env - send an uevent with environmental data121 *122 * @action: action that is happening123 * @kobj: struct kobject that the action is happening to124 * @envp_ext: pointer to environmental data125 *126 * Returns 0 if kobject_uevent_env() is completed with success or the127 * corresponding error when it fails.128 */129int kobject_uevent_env(struct kobject *kobj, enum kobject_action action,130 char *envp_ext[])131{132 struct kobj_uevent_env *env;133 const char *action_string = kobject_actions[action];134 const char *devpath = NULL;135 const char *subsystem;136 struct kobject *top_kobj;137 struct kset *kset;138 const struct kset_uevent_ops *uevent_ops;139 u64 seq;140 int i = 0;141 int retval = 0;142#ifdef CONFIG_NET143 struct uevent_sock *ue_sk;144#endif145146 pr_debug("kobject: '%s' (%p): %s\n",147 kobject_name(kobj), kobj, __func__);148149 /* search the kset we belong to */150 top_kobj = kobj;151 while (!top_kobj->kset && top_kobj->parent)152 top_kobj = top_kobj->parent;153154 if (!top_kobj->kset) {155 pr_debug("kobject: '%s' (%p): %s: attempted to send uevent "156 "without kset!\n", kobject_name(kobj), kobj,157 __func__);158 return -EINVAL;159 }160161 kset = top_kobj->kset;162 uevent_ops = kset->uevent_ops;163164 /* skip the event, if uevent_suppress is set*/165 if (kobj->uevent_suppress) {166 pr_debug("kobject: '%s' (%p): %s: uevent_suppress "167 "caused the event to drop!\n",168 kobject_name(kobj), kobj, __func__);169 return 0;170 }171 /* skip the event, if the filter returns zero. */172 if (uevent_ops && uevent_ops->filter)173 if (!uevent_ops->filter(kset, kobj)) {174 pr_debug("kobject: '%s' (%p): %s: filter function "175 "caused the event to drop!\n",176 kobject_name(kobj), kobj, __func__);177 return 0;178 }179180 /* originating subsystem */181 if (uevent_ops && uevent_ops->name)182 subsystem = uevent_ops->name(kset, kobj);183 else184 subsystem = kobject_name(&kset->kobj);185 if (!subsystem) {186 pr_debug("kobject: '%s' (%p): %s: unset subsystem caused the "187 "event to drop!\n", kobject_name(kobj), kobj,188 __func__);189 return 0;190 }191192 /* environment buffer */193 env = kzalloc(sizeof(struct kobj_uevent_env), GFP_KERNEL);194 if (!env)195 return -ENOMEM;196197 /* complete object path */198 devpath = kobject_get_path(kobj, GFP_KERNEL);199 if (!devpath) {200 retval = -ENOENT;201 goto exit;202 }203204 /* default keys */205 retval = add_uevent_var(env, "ACTION=%s", action_string);206 if (retval)207 goto exit;208 retval = add_uevent_var(env, "DEVPATH=%s", devpath);209 if (retval)210 goto exit;211 retval = add_uevent_var(env, "SUBSYSTEM=%s", subsystem);212 if (retval)213 goto exit;214215 /* keys passed in from the caller */216 if (envp_ext) {217 for (i = 0; envp_ext; i++) {218 retval = add_uevent_var(env, "%s", envp_ext);219 if (retval)220 goto exit;221 }222 }223224 /* let the kset specific function add its stuff */225 if (uevent_ops && uevent_ops->uevent) {226 retval = uevent_ops->uevent(kset, kobj, env);227 if (retval) {228 pr_debug("kobject: '%s' (%p): %s: uevent() returned "229 "%d\n", kobject_name(kobj), kobj,230 __func__, retval);231 goto exit;232 }233 }234235 /*236 * Mark "add" and "remove" events in the object to ensure proper237 * events to userspace during automatic cleanup. If the object did238 * send an "add" event, "remove" will automatically generated by239 * the core, if not already done by the caller.240 */241 if (action == KOBJ_ADD)242 kobj->state_add_uevent_sent = 1;243 else if (action == KOBJ_REMOVE)244 kobj->state_remove_uevent_sent = 1;245246 /* we will send an event, so request a new sequence number */247 spin_lock(&sequence_lock);248 seq = ++uevent_seqnum;249 spin_unlock(&sequence_lock);250 retval = add_uevent_var(env, "SEQNUM=%llu", (unsigned long long)seq);251 if (retval)252 goto exit;253254#if defined(CONFIG_NET)255 /* send netlink message */256 mutex_lock(&uevent_sock_mutex);257 list_for_each_entry(ue_sk, &uevent_sock_list, list) {258 struct sock *uevent_sock = ue_sk->sk;259 struct sk_buff *skb;260 size_t len;261262 /* allocate message with the maximum possible size */263 len = strlen(action_string) + strlen(devpath) + 2;264 skb = alloc_skb(len + env->buflen, GFP_KERNEL);265 if (skb) {266 char *scratch;267268 /* add header */269 scratch = skb_put(skb, len);270 sprintf(scratch, "%s@%s", action_string, devpath);271272 /* copy keys to our continuous event payload buffer */273 for (i = 0; i < env->envp_idx; i++) {274 len = strlen(env->envp) + 1;275 scratch = skb_put(skb, len);276 strcpy(scratch, env->envp);277 }278279 NETLINK_CB(skb).dst_group = 1;280 retval = netlink_broadcast_filtered(uevent_sock, skb,281 0, 1, GFP_KERNEL,282 kobj_bcast_filter,283 kobj);284 /* ENOBUFS should be handled in userspace */285 if (retval == -ENOBUFS)286 retval = 0;287 } else288 retval = -ENOMEM;289 }290 mutex_unlock(&uevent_sock_mutex);291#endif292293 /* call uevent_helper, usually only enabled during early boot */294 if (uevent_helper[0] && !kobj_usermode_filter(kobj)) {295 char *argv [3];296297 argv [0] = uevent_helper;298 argv [1] = (char *)subsystem;299 argv [2] = NULL;300 retval = add_uevent_var(env, "HOME=/");301 if (retval)302 goto exit;303 retval = add_uevent_var(env,304 "PATH=/sbin:/bin:/usr/sbin:/usr/bin");305 if (retval)306 goto exit;307308 retval = call_usermodehelper(argv[0], argv,309 env->envp, UMH_WAIT_EXEC);310 }311312exit:313 kfree(devpath);314 kfree(env);315 return retval;316}
133由参数action取得代表事件类型的字符串。kobject_actions定义如下:[cpp] view plaincopyprint?
- 41 * The actions here must match the index to the string array
42 * in lib/kobject_uevent.c - 43 *
44 * Do not add new actions here without checking with the driver-core - 45 * maintainers. Action strings are not meant to express subsystem
46 * or device specific properties. In most cases you want to send a - 47 * kobject_uevent_env(kobj, KOBJ_CHANGE, env) with additional event
48 * specific variables added to the event environment. - 49 */
50enum kobject_action { - 51 KOBJ_ADD,
52 KOBJ_REMOVE, - 53 KOBJ_CHANGE,
54 KOBJ_MOVE, - 55 KOBJ_ONLINE,
56 KOBJ_OFFLINE, - 57 KOBJ_MAX
58}; - 42/* the strings here must match the enum in include/linux/kobject.h */
43static const char *kobject_actions[] = { - 44 [KOBJ_ADD] = "add",
45 [KOBJ_REMOVE] = "remove", - 46 [KOBJ_CHANGE] = "change",
47 [KOBJ_MOVE] = "move", - 48 [KOBJ_ONLINE] = "online",
49 [KOBJ_OFFLINE] = "offline", - 50};
40/*
40/*41 * The actions here must match the index to the string array42 * in lib/kobject_uevent.c43 *44 * Do not add new actions here without checking with the driver-core45 * maintainers. Action strings are not meant to express subsystem46 * or device specific properties. In most cases you want to send a47 * kobject_uevent_env(kobj, KOBJ_CHANGE, env) with additional event48 * specific variables added to the event environment.49 */50enum kobject_action {51 KOBJ_ADD,52 KOBJ_REMOVE,53 KOBJ_CHANGE,54 KOBJ_MOVE,55 KOBJ_ONLINE,56 KOBJ_OFFLINE,57 KOBJ_MAX58};42/* the strings here must match the enum in include/linux/kobject.h */43static const char *kobject_actions[] = {44 [KOBJ_ADD] = "add",45 [KOBJ_REMOVE] = "remove",46 [KOBJ_CHANGE] = "change",47 [KOBJ_MOVE] = "move",48 [KOBJ_ONLINE] = "online",49 [KOBJ_OFFLINE] = "offline",50};
149 - 162行,因为只有kset才包含处理uevent的函数,即kset.uevent_ops,所以这里查找kobj所属的kset,如果kobj->kset不存在,就沿着kobj->parent向上查找,直到找到一个不为空的kset为止。如果确实没有找到kset,则退出。165 - 170行,如果kobj->uevent_suppress的值为1,表示禁止发出uevent事件,退出。172 - 178行,如果uevent_ops不为空,并且实现了uevent_ops->filter,则执行uevent_ops->filter,如果uevent_ops->filter返回值为0,表示这个uevent被过滤了,退出。181 - 190行,如果uevent_ops不为空,并且实现了uevent_ops->name,则通过uevent_ops->name获得子系统名,如果uevent_ops为空,或者没有实现uevent_ops->name,则以kset->kobj的名字作为子系统名。193行,创建kobj_uevent_env结构体变量env,用来保存环境变量。198行,通过调用kobject_get_path函数取得kobj在/sys系统中的路径,保存在devpath变量中。205 - 213行,通过调用add_uevent_var函数将事件名,kobj路径和子系统名加入到环境变量env中。216 - 222行,如果有通过参数传递的环境变量,也调用add_uevent_var函数加入到环境变量env中。225 - 233行,如果uevent_ops不为空,并且实现了uevent_ops->uevent函数,则调用uevent_ops->uevent。241 - 244行,如果要发送的事件是KOBJ_ADD或KOBJ_REMOVE,则相应将kobj->state_add_uevent_sent或kobj->state_remove_uevent_sent置为1。247 - 252行,将发送事件序列数加1,添加到环境变量env中。254 - 291行,条件编译部分我们不分析。294行,先来看uevent_helper的定义:char uevent_helper[UEVENT_HELPER_PATH_LEN] = CONFIG_UEVENT_HELPER_PATH;#define UEVENT_HELPER_PATH_LEN 256CONFIG_UEVENT_HELPER_PATH="/sbin/hotplug"所以uevent_helper就是"/sbin/hotplug"。300 - 306行,将HOME和PATH加入环境变量env中。308 - 309行,执行用户空间的/sbin/hotplug程序,传递环境变量为env。至此, kobject_uevent_env -> kobject_uevent -> kset_register -> kset_create_and_add函数就分析完了,kset被创建和注册到系统中。
