Linux设备模型分析之kobject--转
时间:10-02
整理:3721RD
点击:
Linux设备模型分析之kobject --转
一、kobject应用举例linux设备模型最基本的组成元素是kobject,我们先来看一个kobject的应用例子,该程序在Ubuntu 10.10, 2.6.32-38-generic-pae内核上调试通过。[cpp] view plaincopyprint?
#include <linux/device.h>#include <linux/module.h>#include <linux/kernel.h>#include <linux/init.h>#include <linux/string.h>#include <linux/sysfs.h>#include <linux/stat.h>MODULE_AUTHOR("haoyu");MODULE_LICENSE("Dual BSD/GPL");struct my_kobject{ int value; struct kobject kobj;}; struct my_kobject my_kobj;void kobject_release(struct kobject *kobject);ssize_t kobject_attr_show(struct kobject *kobject, struct attribute *attr,char *buf);ssize_t kobject_attr_store(struct kobject *kobject,struct attribute *attr,const char *buf, size_t count);struct attribute kobject_attr1 = { .name = "name", .mode = S_IRWXUGO,};struct attribute kobject_attr2 = { .name = "value", .mode = S_IRWXUGO,};static struct attribute *kobject_def_attrs[] = { &kobject_attr1, &kobject_attr2, NULL,};struct sysfs_ops kobject_sysfs_ops ={ .show = kobject_attr_show, .store = kobject_attr_store,};struct kobj_type ktype ={ .release = kobject_release, .sysfs_ops = &kobject_sysfs_ops, .default_attrs = kobject_def_attrs,};void kobject_release(struct kobject *kobject){ printk("kobject release.\n");}ssize_t kobject_attr_show(struct kobject *kobject, struct attribute *attr,char *buf){ int count = 0; struct my_kobject *my_kobj = container_of(kobject, struct my_kobject, kobj); printk("kobject attribute show.\n"); if(strcmp(attr->name, "name") == 0) count = sprintf(buf, "%s\n", kobject->name); else if(strcmp(attr->name, "value") == 0) count = sprintf(buf, "%d\n", my_kobj->value); else printk("no this attribute.\n"); return count;}ssize_t kobject_attr_store(struct kobject *kobject,struct attribute *attr,const char *buf, size_t count){ int val; struct my_kobject *my_kobj = container_of(kobject, struct my_kobject, kobj); printk("kobject attribute store.\n"); if(strcmp(attr->name, "name") == 0) printk("Can not change name.\n"); else if(strcmp(attr->name, "value") == 0) { val = buf[0] - '0'; if(val == 0 || val == 1) my_kobj->value = val; else printk("value is '0' or '1'\n"); } else printk("no this attribute.\n"); return count;}static int kobject_test_init(void){ printk("kboject test init.\n"); kobject_init_and_add(&my_kobj.kobj,&ktype,NULL,"kobject_test"); return 0;}static void kobject_test_exit(void){ printk("kobject test exit.\n"); kobject_del(&my_kobj.kobj);}module_init(kobject_test_init);module_exit(kobject_test_exit);
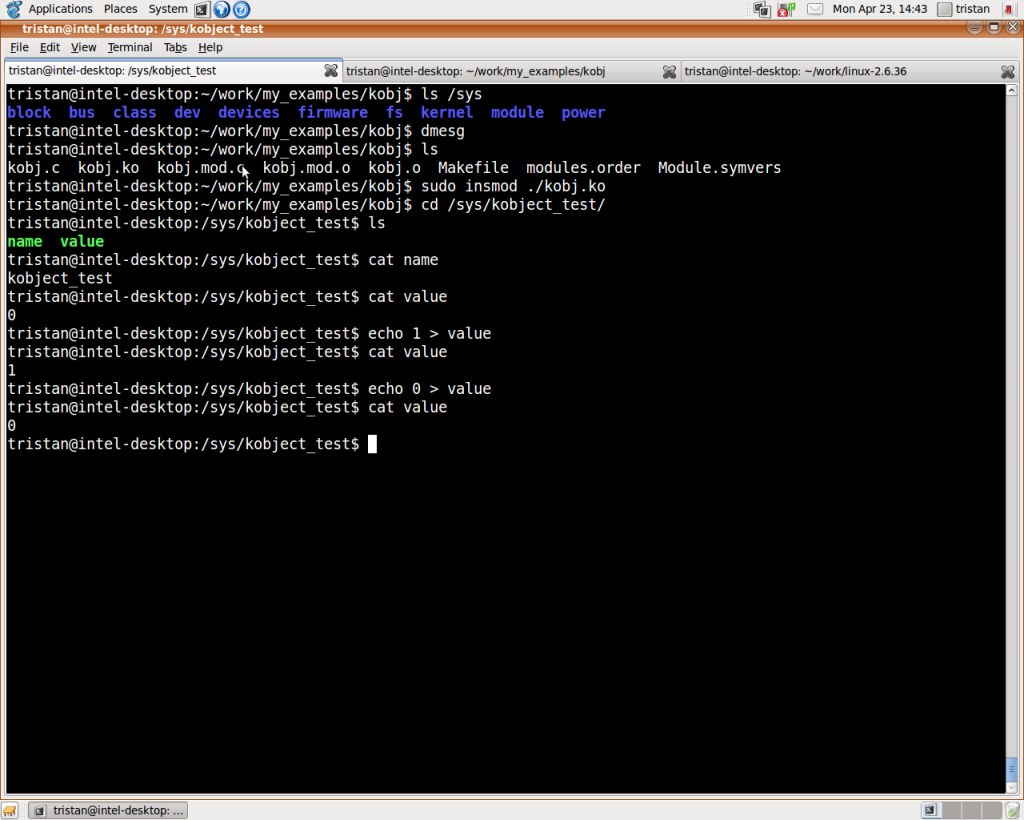
该模块执行过程如下图所示:
 二、相关数据结构:kobject是Linux设备模型中最基本的数据结构,代表设备模式的一个基本对象。kobj_type是kobject的类型,包括kobject的属性以及属性的操作接口,不同的kobject可以具有相同的kobj_type。kset是几个kobject的集合,这些kobject可以具有相同的kobj_type,也可以具有不同的kobj_type。[cpp] view plaincopyprint?
二、相关数据结构:kobject是Linux设备模型中最基本的数据结构,代表设备模式的一个基本对象。kobj_type是kobject的类型,包括kobject的属性以及属性的操作接口,不同的kobject可以具有相同的kobj_type。kset是几个kobject的集合,这些kobject可以具有相同的kobj_type,也可以具有不同的kobj_type。[cpp] view plaincopyprint?
struct kobject { const char *name; struct list_head entry; struct kobject *parent; struct kset *kset; struct kobj_type *ktype; struct sysfs_dirent *sd; struct kref kref; unsigned int state_initialized:1; unsigned int state_in_sysfs:1; unsigned int state_add_uevent_sent:1; unsigned int state_remove_uevent_sent:1; unsigned int uevent_suppress:1;}; /** * struct kset - a set of kobjects of a specific type, belonging to a specific subsystem. * * A kset defines a group of kobjects. They can be individually * different "types" but overall these kobjects all want to be grouped * together and operated on in the same manner. ksets are used to * define the attribute callbacks and other common events that happen to * a kobject. * * @list: the list of all kobjects for this kset * @list_lock: a lock for iterating over the kobjects * @kobj: the embedded kobject for this kset (recursion, isn't it fun...) * @uevent_ops: the set of uevent operations for this kset. These are * called whenever a kobject has something happen to it so that the kset * can add new environment variables, or filter out the uevents if so * desired. */struct kset { struct list_head list; spinlock_t list_lock; struct kobject kobj; const struct kset_uevent_ops *uevent_ops;}; struct kset_uevent_ops { int (* const filter)(struct kset *kset, struct kobject *kobj); const char *(* const name)(struct kset *kset, struct kobject *kobj); int (* const uevent)(struct kset *kset, struct kobject *kobj, struct kobj_uevent_env *env);}; struct kobj_type { void (*release)(struct kobject *kobj); const struct sysfs_ops *sysfs_ops; struct attribute **default_attrs; const struct kobj_ns_type_operations *(*child_ns_type)(struct kobject *kobj); const void *(*namespace)(struct kobject *kobj);}; struct sysfs_ops { ssize_t (*show)(struct kobject *, struct attribute *,char *); ssize_t (*store)(struct kobject *,struct attribute *,const char *, size_t);}; struct attribute { const char *name; mode_t mode;#ifdef CONFIG_DEBUG_LOCK_ALLOC struct lock_class_key *key; struct lock_class_key skey;#endif}; /* * Callbacks so sysfs can determine namespaces * @current_ns: return calling task's namespace * @netlink_ns: return namespace to which a sock belongs (right?) * @initial_ns: return the initial namespace (i.e. init_net_ns) */struct kobj_ns_type_operations { enum kobj_ns_type type; const void *(*current_ns)(void); const void *(*netlink_ns)(struct sock *sk); const void *(*initial_ns)(void);}; struct kref { atomic_t refcount;};
三、kobject注册和注销过程分析kobject的注册是通过调用kobject_init_and_add函数,该函数定义如下:[cpp] view plaincopyprint?
/** * kobject_init_and_add - initialize a kobject structure and add it to the kobject hierarchy * @kobj: pointer to the kobject to initialize * @ktype: pointer to the ktype for this kobject. * @parent: pointer to the parent of this kobject. * @fmt: the name of the kobject. * * This function combines the call to kobject_init() and * kobject_add(). The same type of error handling after a call to * kobject_add() and kobject lifetime rules are the same here. */int kobject_init_and_add(struct kobject *kobj, struct kobj_type *ktype, struct kobject *parent, const char *fmt, ...){ va_list args; int retval; kobject_init(kobj, ktype); va_start(args, fmt); retval = kobject_add_varg(kobj, parent, fmt, args); va_end(args); return retval;}
这个函数分为两部分,首先调用kobject_init函数对kobject对象进行基本的初始化。然后,调用kobject_add_varg函数将kobject注册到系统中。va_start和va_end是处理可变参数的固定语法。先来看kobject_init,该函数定义如下:[cpp] view plaincopyprint?
/** * kobject_init - initialize a kobject structure * @kobj: pointer to the kobject to initialize * @ktype: pointer to the ktype for this kobject. * * This function will properly initialize a kobject such that it can then * be passed to the kobject_add() call. * * After this function is called, the kobject MUST be cleaned up by a call * to kobject_put(), not by a call to kfree directly to ensure that all of * the memory is cleaned up properly. */void kobject_init(struct kobject *kobj, struct kobj_type *ktype){ char *err_str; if (!kobj) { err_str = "invalid kobject pointer!"; goto error; } if (!ktype) { err_str = "must have a ktype to be initialized properly!\n"; goto error; } if (kobj->state_initialized) { /* do not error out as sometimes we can recover */ printk(KERN_ERR "kobject (%p): tried to init an initialized " "object, something is seriously wrong.\n", kobj); dump_stack(); } kobject_init_internal(kobj); kobj->ktype = ktype; return; error: printk(KERN_ERR "kobject (%p): %s\n", kobj, err_str); dump_stack();}
该函数首先确保kobj和ktype都存在,否则直接退出。如果该kobj进行过初始化,则打印警告信息。然后调用kobject_init_internal真正开始初始化kobj,最后把kobj->ktype设置为ktype。kobject_init_internal函数定义如下:[cpp] view plaincopyprint?
static void kobject_init_internal(struct kobject *kobj){ if (!kobj) return; kref_init(&kobj->kref); INIT_LIST_HEAD(&kobj->entry); kobj->state_in_sysfs = 0; kobj->state_add_uevent_sent = 0; kobj->state_remove_uevent_sent = 0; kobj->state_initialized = 1;}
首先初始化kobj->kref,实际上kobj->kref就是一个原子变量(atomic_t)。接着初始化链表项kobj->entry,并设置其他kobject成员。至此,kobject_init函数就分析完了,我们返回到kobject_init_and_add函数,下面该分析kobject_add_varg函数了:[cpp] view plaincopyprint?
static int kobject_add_varg(struct kobject *kobj, struct kobject *parent, const char *fmt, va_list vargs){ int retval; retval = kobject_set_name_vargs(kobj, fmt, vargs); if (retval) { printk(KERN_ERR "kobject: can not set name properly!\n"); return retval; } kobj->parent = parent; return kobject_add_internal(kobj);}
首先调用kobject_set_name_vargs设置kob->name。然后初始化kobj->parent为parent参数指定的kobject。最后,调用kobject_add_internal将kobject注册到系统中,该函数定义如下:[cpp] view plaincopyprint?
static int kobject_add_internal(struct kobject *kobj){ int error = 0; struct kobject *parent; if (!kobj) return -ENOENT; if (!kobj->name || !kobj->name[0]) { WARN(1, "kobject: (%p): attempted to be registered with empty " "name!\n", kobj); return -EINVAL; } parent = kobject_get(kobj->parent); /* join kset if set, use it as parent if we do not already have one */ if (kobj->kset) { if (!parent) parent = kobject_get(&kobj->kset->kobj); kobj_kset_join(kobj); kobj->parent = parent; } pr_debug("kobject: '%s' (%p): %s: parent: '%s', set: '%s'\n", kobject_name(kobj), kobj, __func__, parent ? kobject_name(parent) : "<NULL>", kobj->kset ? kobject_name(&kobj->kset->kobj) : "<NULL>"); error = create_dir(kobj); if (error) { kobj_kset_leave(kobj); kobject_put(parent); kobj->parent = NULL; /* be noisy on error issues */ if (error == -EEXIST) printk(KERN_ERR "%s failed for %s with " "-EEXIST, don't try to register things with " "the same name in the same directory.\n", __func__, kobject_name(kobj)); else printk(KERN_ERR "%s failed for %s (%d)\n", __func__, kobject_name(kobj), error); dump_stack(); } else kobj->state_in_sysfs = 1; return error;}
首先确保kobj->name已经被赋值,即kobject必须有名字。如果指定了kobj->kset,则调用kobj_kset_join将kobj加入到kobj->kset中。同时,如果kobj->parent仍为NULL,则将kobj->parent设置为kobj->kset->kobj。然后,调用create_dir(kobj)在/sys目录下建立kobject相关目录结构。kobj_kset_join函数定义如下:[cpp] view plaincopyprint?
/* add the kobject to its kset's list */static void kobj_kset_join(struct kobject *kobj){ if (!kobj->kset) return; kset_get(kobj->kset); spin_lock(&kobj->kset->list_lock); list_add_tail(&kobj->entry, &kobj->kset->list); spin_unlock(&kobj->kset->list_lock);}
create_dir函数定义如下:[cpp] view plaincopyprint?
static int create_dir(struct kobject *kobj){ int error = 0; if (kobject_name(kobj)) { error = sysfs_create_dir(kobj); if (!error) { error = populate_dir(kobj); if (error) sysfs_remove_dir(kobj); } } return error;}
首先调用sysfs_create_dir在/sys下建立目录,然后再调用populate_dir在新建目录下生成属性文件。sysfs_create_dir函数定义如下:[cpp] view plaincopyprint?
/** * sysfs_create_dir - create a directory for an object. * @kobj: object we're creating directory for. */int sysfs_create_dir(struct kobject * kobj){ enum kobj_ns_type type; struct sysfs_dirent *parent_sd, *sd; const void *ns = NULL; int error = 0; BUG_ON(!kobj); if (kobj->parent) parent_sd = kobj->parent->sd; else parent_sd = &sysfs_root; if (sysfs_ns_type(parent_sd)) ns = kobj->ktype->namespace(kobj); type = sysfs_read_ns_type(kobj); error = create_dir(kobj, parent_sd, type, ns, kobject_name(kobj), &sd); if (!error) kobj->sd = sd; return error;}
这里主要是通过调用create_dir函数建立kobject对应的目录。这个函数我们就不继续向下跟踪了。下面来看populate_dir函数,其定义如下:[cpp] view plaincopyprint?
/* * populate_dir - populate directory with attributes. * @kobj: object we're working on. * * Most subsystems have a set of default attributes that are associated * with an object that registers with them. This is a helper called during * object registration that loops through the default attributes of the * subsystem and creates attributes files for them in sysfs. */static int populate_dir(struct kobject *kobj){ struct kobj_type *t = get_ktype(kobj); struct attribute *attr; int error = 0; int i; if (t && t->default_attrs) { for (i = 0; (attr = t->default_attrs) != NULL; i++) { error = sysfs_create_file(kobj, attr); if (error) break; } } return error;}
该函数循环遍历kobject的所有属性,并调用sysfs_create_file函数在/sys系统对应目录下建立属性文件。至此,kobject的注册过程我们就分析完了。kobject的注销过程是调用kobject_del函数,该函数定义如下:[cpp] view plaincopyprint?
/** * kobject_del - unlink kobject from hierarchy. * @kobj: object. */void kobject_del(struct kobject *kobj){ if (!kobj) return; sysfs_remove_dir(kobj); kobj->state_in_sysfs = 0; kobj_kset_leave(kobj); kobject_put(kobj->parent); kobj->parent = NULL;}
这里需要注意的是,只要把目录删除,目录下的属性文件自动就删除了。
一、kobject应用举例linux设备模型最基本的组成元素是kobject,我们先来看一个kobject的应用例子,该程序在Ubuntu 10.10, 2.6.32-38-generic-pae内核上调试通过。[cpp] view plaincopyprint?
- #include <linux/module.h>
#include <linux/kernel.h> - #include <linux/init.h>
#include <linux/string.h> - #include <linux/sysfs.h>
#include <linux/stat.h> -
MODULE_AUTHOR("haoyu"); - MODULE_LICENSE("Dual BSD/GPL");
- struct my_kobject
{ - int value;
struct kobject kobj; - };
- struct my_kobject my_kobj;
- void kobject_release(struct kobject *kobject);
ssize_t kobject_attr_show(struct kobject *kobject, struct attribute *attr,char *buf); - ssize_t kobject_attr_store(struct kobject *kobject,struct attribute *attr,const char *buf, size_t count);
- struct attribute kobject_attr1 = {
.name = "name", - .mode = S_IRWXUGO,
}; -
struct attribute kobject_attr2 = { - .name = "value",
.mode = S_IRWXUGO, - };
- static struct attribute *kobject_def_attrs[] = {
&kobject_attr1, - &kobject_attr2,
NULL, - };
- struct sysfs_ops kobject_sysfs_ops =
{ - .show = kobject_attr_show,
.store = kobject_attr_store, - };
- struct kobj_type ktype =
{ - .release = kobject_release,
.sysfs_ops = &kobject_sysfs_ops, - .default_attrs = kobject_def_attrs,
}; -
void kobject_release(struct kobject *kobject) - {
printk("kobject release.\n"); - }
- ssize_t kobject_attr_show(struct kobject *kobject, struct attribute *attr,char *buf)
{ - int count = 0;
struct my_kobject *my_kobj = container_of(kobject, struct my_kobject, kobj); - printk("kobject attribute show.\n");
if(strcmp(attr->name, "name") == 0) - count = sprintf(buf, "%s\n", kobject->name);
else if(strcmp(attr->name, "value") == 0) - count = sprintf(buf, "%d\n", my_kobj->value);
else - printk("no this attribute.\n");
- return count;
} -
ssize_t kobject_attr_store(struct kobject *kobject,struct attribute *attr,const char *buf, size_t count) - {
int val; - struct my_kobject *my_kobj = container_of(kobject, struct my_kobject, kobj);
printk("kobject attribute store.\n"); - if(strcmp(attr->name, "name") == 0)
printk("Can not change name.\n"); - else if(strcmp(attr->name, "value") == 0)
{ - val = buf[0] - '0';
if(val == 0 || val == 1) - my_kobj->value = val;
else - printk("value is '0' or '1'\n");
} - else
printk("no this attribute.\n"); -
return count; - }
- static int kobject_test_init(void)
{ - printk("kboject test init.\n");
kobject_init_and_add(&my_kobj.kobj,&ktype,NULL,"kobject_test"); - return 0;
} -
static void kobject_test_exit(void) - {
printk("kobject test exit.\n"); - kobject_del(&my_kobj.kobj);
} -
module_init(kobject_test_init); - module_exit(kobject_test_exit);
#include <linux/device.h>
#include <linux/device.h>#include <linux/module.h>#include <linux/kernel.h>#include <linux/init.h>#include <linux/string.h>#include <linux/sysfs.h>#include <linux/stat.h>MODULE_AUTHOR("haoyu");MODULE_LICENSE("Dual BSD/GPL");struct my_kobject{ int value; struct kobject kobj;}; struct my_kobject my_kobj;void kobject_release(struct kobject *kobject);ssize_t kobject_attr_show(struct kobject *kobject, struct attribute *attr,char *buf);ssize_t kobject_attr_store(struct kobject *kobject,struct attribute *attr,const char *buf, size_t count);struct attribute kobject_attr1 = { .name = "name", .mode = S_IRWXUGO,};struct attribute kobject_attr2 = { .name = "value", .mode = S_IRWXUGO,};static struct attribute *kobject_def_attrs[] = { &kobject_attr1, &kobject_attr2, NULL,};struct sysfs_ops kobject_sysfs_ops ={ .show = kobject_attr_show, .store = kobject_attr_store,};struct kobj_type ktype ={ .release = kobject_release, .sysfs_ops = &kobject_sysfs_ops, .default_attrs = kobject_def_attrs,};void kobject_release(struct kobject *kobject){ printk("kobject release.\n");}ssize_t kobject_attr_show(struct kobject *kobject, struct attribute *attr,char *buf){ int count = 0; struct my_kobject *my_kobj = container_of(kobject, struct my_kobject, kobj); printk("kobject attribute show.\n"); if(strcmp(attr->name, "name") == 0) count = sprintf(buf, "%s\n", kobject->name); else if(strcmp(attr->name, "value") == 0) count = sprintf(buf, "%d\n", my_kobj->value); else printk("no this attribute.\n"); return count;}ssize_t kobject_attr_store(struct kobject *kobject,struct attribute *attr,const char *buf, size_t count){ int val; struct my_kobject *my_kobj = container_of(kobject, struct my_kobject, kobj); printk("kobject attribute store.\n"); if(strcmp(attr->name, "name") == 0) printk("Can not change name.\n"); else if(strcmp(attr->name, "value") == 0) { val = buf[0] - '0'; if(val == 0 || val == 1) my_kobj->value = val; else printk("value is '0' or '1'\n"); } else printk("no this attribute.\n"); return count;}static int kobject_test_init(void){ printk("kboject test init.\n"); kobject_init_and_add(&my_kobj.kobj,&ktype,NULL,"kobject_test"); return 0;}static void kobject_test_exit(void){ printk("kobject test exit.\n"); kobject_del(&my_kobj.kobj);}module_init(kobject_test_init);module_exit(kobject_test_exit);
该模块执行过程如下图所示:
 二、相关数据结构:kobject是Linux设备模型中最基本的数据结构,代表设备模式的一个基本对象。kobj_type是kobject的类型,包括kobject的属性以及属性的操作接口,不同的kobject可以具有相同的kobj_type。kset是几个kobject的集合,这些kobject可以具有相同的kobj_type,也可以具有不同的kobj_type。[cpp] view plaincopyprint?
二、相关数据结构:kobject是Linux设备模型中最基本的数据结构,代表设备模式的一个基本对象。kobj_type是kobject的类型,包括kobject的属性以及属性的操作接口,不同的kobject可以具有相同的kobj_type。kset是几个kobject的集合,这些kobject可以具有相同的kobj_type,也可以具有不同的kobj_type。[cpp] view plaincopyprint?- const char *name;
struct list_head entry; - struct kobject *parent;
struct kset *kset; - struct kobj_type *ktype;
struct sysfs_dirent *sd; - struct kref kref;
unsigned int state_initialized:1; - unsigned int state_in_sysfs:1;
unsigned int state_add_uevent_sent:1; - unsigned int state_remove_uevent_sent:1;
unsigned int uevent_suppress:1; - };
- /**
* struct kset - a set of kobjects of a specific type, belonging to a specific subsystem. - *
* A kset defines a group of kobjects. They can be individually - * different "types" but overall these kobjects all want to be grouped
* together and operated on in the same manner. ksets are used to - * define the attribute callbacks and other common events that happen to
* a kobject. - *
* @list: the list of all kobjects for this kset - * @list_lock: a lock for iterating over the kobjects
* @kobj: the embedded kobject for this kset (recursion, isn't it fun...) - * @uevent_ops: the set of uevent operations for this kset. These are
* called whenever a kobject has something happen to it so that the kset - * can add new environment variables, or fiLTEr out the uevents if so
* desired. - */
struct kset { - struct list_head list;
SPInlock_t list_lock; - struct kobject kobj;
const struct kset_uevent_ops *uevent_ops; - };
- struct kset_uevent_ops {
int (* const filter)(struct kset *kset, struct kobject *kobj); - const char *(* const name)(struct kset *kset, struct kobject *kobj);
int (* const uevent)(struct kset *kset, struct kobject *kobj, - struct kobj_uevent_env *env);
}; -
struct kobj_type { - void (*release)(struct kobject *kobj);
const struct sysfs_ops *sysfs_ops; - struct attribute **default_attrs;
const struct kobj_ns_type_operations *(*child_ns_type)(struct kobject *kobj); - const void *(*namespace)(struct kobject *kobj);
}; -
struct sysfs_ops { - ssize_t (*show)(struct kobject *, struct attribute *,char *);
ssize_t (*store)(struct kobject *,struct attribute *,const char *, size_t); - };
- struct attribute {
const char *name; - mode_t mode;
#ifdef CONFIG_DEBUG_LOCK_ALLOC - struct lock_class_key *key;
struct lock_class_key skey; - #endif
}; -
/* - * Callbacks so sysfs can determine namespaces
* @current_ns: return calling task's namespace - * @netlink_ns: return namespace to which a sock belongs (right?)
* @initial_ns: return the initial namespace (i.e. init_net_ns) - */
struct kobj_ns_type_operations { - enum kobj_ns_type type;
const void *(*current_ns)(void); - const void *(*netlink_ns)(struct sock *sk);
const void *(*initial_ns)(void); - };
- struct kref {
atoMIC_t refcount; - };
struct kobject {
struct kobject { const char *name; struct list_head entry; struct kobject *parent; struct kset *kset; struct kobj_type *ktype; struct sysfs_dirent *sd; struct kref kref; unsigned int state_initialized:1; unsigned int state_in_sysfs:1; unsigned int state_add_uevent_sent:1; unsigned int state_remove_uevent_sent:1; unsigned int uevent_suppress:1;}; /** * struct kset - a set of kobjects of a specific type, belonging to a specific subsystem. * * A kset defines a group of kobjects. They can be individually * different "types" but overall these kobjects all want to be grouped * together and operated on in the same manner. ksets are used to * define the attribute callbacks and other common events that happen to * a kobject. * * @list: the list of all kobjects for this kset * @list_lock: a lock for iterating over the kobjects * @kobj: the embedded kobject for this kset (recursion, isn't it fun...) * @uevent_ops: the set of uevent operations for this kset. These are * called whenever a kobject has something happen to it so that the kset * can add new environment variables, or filter out the uevents if so * desired. */struct kset { struct list_head list; spinlock_t list_lock; struct kobject kobj; const struct kset_uevent_ops *uevent_ops;}; struct kset_uevent_ops { int (* const filter)(struct kset *kset, struct kobject *kobj); const char *(* const name)(struct kset *kset, struct kobject *kobj); int (* const uevent)(struct kset *kset, struct kobject *kobj, struct kobj_uevent_env *env);}; struct kobj_type { void (*release)(struct kobject *kobj); const struct sysfs_ops *sysfs_ops; struct attribute **default_attrs; const struct kobj_ns_type_operations *(*child_ns_type)(struct kobject *kobj); const void *(*namespace)(struct kobject *kobj);}; struct sysfs_ops { ssize_t (*show)(struct kobject *, struct attribute *,char *); ssize_t (*store)(struct kobject *,struct attribute *,const char *, size_t);}; struct attribute { const char *name; mode_t mode;#ifdef CONFIG_DEBUG_LOCK_ALLOC struct lock_class_key *key; struct lock_class_key skey;#endif}; /* * Callbacks so sysfs can determine namespaces * @current_ns: return calling task's namespace * @netlink_ns: return namespace to which a sock belongs (right?) * @initial_ns: return the initial namespace (i.e. init_net_ns) */struct kobj_ns_type_operations { enum kobj_ns_type type; const void *(*current_ns)(void); const void *(*netlink_ns)(struct sock *sk); const void *(*initial_ns)(void);}; struct kref { atomic_t refcount;};
三、kobject注册和注销过程分析kobject的注册是通过调用kobject_init_and_add函数,该函数定义如下:[cpp] view plaincopyprint?
- * kobject_init_and_add - initialize a kobject structure and add it to the kobject hierarchy
* @kobj: pointer to the kobject to initialize - * @ktype: pointer to the ktype for this kobject.
* @parent: pointer to the parent of this kobject. - * @fmt: the name of the kobject.
* - * This function combines the call to kobject_init() and
* kobject_add(). The same type of error handling after a call to - * kobject_add() and kobject lifetime rules are the same here.
*/ - int kobject_init_and_add(struct kobject *kobj, struct kobj_type *ktype,
struct kobject *parent, const char *fmt, ...) - {
va_list args; - int retval;
- kobject_init(kobj, ktype);
- va_start(args, fmt);
retval = kobject_add_varg(kobj, parent, fmt, args); - va_end(args);
- return retval;
- }
/**
/** * kobject_init_and_add - initialize a kobject structure and add it to the kobject hierarchy * @kobj: pointer to the kobject to initialize * @ktype: pointer to the ktype for this kobject. * @parent: pointer to the parent of this kobject. * @fmt: the name of the kobject. * * This function combines the call to kobject_init() and * kobject_add(). The same type of error handling after a call to * kobject_add() and kobject lifetime rules are the same here. */int kobject_init_and_add(struct kobject *kobj, struct kobj_type *ktype, struct kobject *parent, const char *fmt, ...){ va_list args; int retval; kobject_init(kobj, ktype); va_start(args, fmt); retval = kobject_add_varg(kobj, parent, fmt, args); va_end(args); return retval;}
这个函数分为两部分,首先调用kobject_init函数对kobject对象进行基本的初始化。然后,调用kobject_add_varg函数将kobject注册到系统中。va_start和va_end是处理可变参数的固定语法。先来看kobject_init,该函数定义如下:[cpp] view plaincopyprint?
- * kobject_init - initialize a kobject structure
* @kobj: pointer to the kobject to initialize - * @ktype: pointer to the ktype for this kobject.
* - * This function will properly initialize a kobject such that it can then
* be passed to the kobject_add() call. - *
* After this function is called, the kobject MUST be cleaned up by a call - * to kobject_put(), not by a call to kfree directly to ensure that all of
* the memory is cleaned up properly. - */
void kobject_init(struct kobject *kobj, struct kobj_type *ktype) - {
char *err_str; -
if (!kobj) { - err_str = "invalid kobject pointer!";
goto error; - }
if (!ktype) { - err_str = "must have a ktype to be initialized properly!\n";
goto error; - }
if (kobj->state_initialized) { - /* do not error out as sometimes we can recover */
printk(KERN_ERR "kobject (%p): tried to init an initialized " - "object, something is seriously wrong.\n", kobj);
dump_stack(); - }
- kobject_init_internal(kobj);
kobj->ktype = ktype; - return;
- error:
printk(KERN_ERR "kobject (%p): %s\n", kobj, err_str); - dump_stack();
- }
/**
/** * kobject_init - initialize a kobject structure * @kobj: pointer to the kobject to initialize * @ktype: pointer to the ktype for this kobject. * * This function will properly initialize a kobject such that it can then * be passed to the kobject_add() call. * * After this function is called, the kobject MUST be cleaned up by a call * to kobject_put(), not by a call to kfree directly to ensure that all of * the memory is cleaned up properly. */void kobject_init(struct kobject *kobj, struct kobj_type *ktype){ char *err_str; if (!kobj) { err_str = "invalid kobject pointer!"; goto error; } if (!ktype) { err_str = "must have a ktype to be initialized properly!\n"; goto error; } if (kobj->state_initialized) { /* do not error out as sometimes we can recover */ printk(KERN_ERR "kobject (%p): tried to init an initialized " "object, something is seriously wrong.\n", kobj); dump_stack(); } kobject_init_internal(kobj); kobj->ktype = ktype; return; error: printk(KERN_ERR "kobject (%p): %s\n", kobj, err_str); dump_stack();}
该函数首先确保kobj和ktype都存在,否则直接退出。如果该kobj进行过初始化,则打印警告信息。然后调用kobject_init_internal真正开始初始化kobj,最后把kobj->ktype设置为ktype。kobject_init_internal函数定义如下:[cpp] view plaincopyprint?
- {
if (!kobj) - return;
kref_init(&kobj->kref); - INIT_LIST_HEAD(&kobj->entry);
kobj->state_in_sysfs = 0; - kobj->state_add_uevent_sent = 0;
kobj->state_remove_uevent_sent = 0; - kobj->state_initialized = 1;
- }
static void kobject_init_internal(struct kobject *kobj)
static void kobject_init_internal(struct kobject *kobj){ if (!kobj) return; kref_init(&kobj->kref); INIT_LIST_HEAD(&kobj->entry); kobj->state_in_sysfs = 0; kobj->state_add_uevent_sent = 0; kobj->state_remove_uevent_sent = 0; kobj->state_initialized = 1;}
首先初始化kobj->kref,实际上kobj->kref就是一个原子变量(atomic_t)。接着初始化链表项kobj->entry,并设置其他kobject成员。至此,kobject_init函数就分析完了,我们返回到kobject_init_and_add函数,下面该分析kobject_add_varg函数了:[cpp] view plaincopyprint?
- const char *fmt, va_list vargs)
{ - int retval;
- retval = kobject_set_name_vargs(kobj, fmt, vargs);
if (retval) { - printk(KERN_ERR "kobject: can not set name properly!\n");
return retval; - }
kobj->parent = parent; - return kobject_add_internal(kobj);
- }
static int kobject_add_varg(struct kobject *kobj, struct kobject *parent,
static int kobject_add_varg(struct kobject *kobj, struct kobject *parent, const char *fmt, va_list vargs){ int retval; retval = kobject_set_name_vargs(kobj, fmt, vargs); if (retval) { printk(KERN_ERR "kobject: can not set name properly!\n"); return retval; } kobj->parent = parent; return kobject_add_internal(kobj);}
首先调用kobject_set_name_vargs设置kob->name。然后初始化kobj->parent为parent参数指定的kobject。最后,调用kobject_add_internal将kobject注册到系统中,该函数定义如下:[cpp] view plaincopyprint?
- {
int error = 0; - struct kobject *parent;
- if (!kobj)
return -ENOENT; -
if (!kobj->name || !kobj->name[0]) { - WARN(1, "kobject: (%p): attempted to be registered with empty "
"name!\n", kobj); - return -EINVAL;
} -
parent = kobject_get(kobj->parent); -
/* join kset if set, use it as parent if we do not already have one */ - if (kobj->kset) {
if (!parent) - parent = kobject_get(&kobj->kset->kobj);
kobj_kset_join(kobj); - kobj->parent = parent;
} -
pr_debug("kobject: '%s' (%p): %s: parent: '%s', set: '%s'\n", - kobject_name(kobj), kobj, __func__,
parent ? kobject_name(parent) : "<NULL>", - kobj->kset ? kobject_name(&kobj->kset->kobj) : "<NULL>");
- error = create_dir(kobj);
if (error) { - kobj_kset_leave(kobj);
kobject_put(parent); - kobj->parent = NULL;
- /* be noisy on error issues */
if (error == -EEXIST) - printk(KERN_ERR "%s failed for %s with "
"-EEXIST, don't try to register things with " - "the same name in the same directory.\n",
__func__, kobject_name(kobj)); - else
printk(KERN_ERR "%s failed for %s (%d)\n", - __func__, kobject_name(kobj), error);
dump_stack(); - } else
kobj->state_in_sysfs = 1; -
return error; - }
static int kobject_add_internal(struct kobject *kobj)
static int kobject_add_internal(struct kobject *kobj){ int error = 0; struct kobject *parent; if (!kobj) return -ENOENT; if (!kobj->name || !kobj->name[0]) { WARN(1, "kobject: (%p): attempted to be registered with empty " "name!\n", kobj); return -EINVAL; } parent = kobject_get(kobj->parent); /* join kset if set, use it as parent if we do not already have one */ if (kobj->kset) { if (!parent) parent = kobject_get(&kobj->kset->kobj); kobj_kset_join(kobj); kobj->parent = parent; } pr_debug("kobject: '%s' (%p): %s: parent: '%s', set: '%s'\n", kobject_name(kobj), kobj, __func__, parent ? kobject_name(parent) : "<NULL>", kobj->kset ? kobject_name(&kobj->kset->kobj) : "<NULL>"); error = create_dir(kobj); if (error) { kobj_kset_leave(kobj); kobject_put(parent); kobj->parent = NULL; /* be noisy on error issues */ if (error == -EEXIST) printk(KERN_ERR "%s failed for %s with " "-EEXIST, don't try to register things with " "the same name in the same directory.\n", __func__, kobject_name(kobj)); else printk(KERN_ERR "%s failed for %s (%d)\n", __func__, kobject_name(kobj), error); dump_stack(); } else kobj->state_in_sysfs = 1; return error;}
首先确保kobj->name已经被赋值,即kobject必须有名字。如果指定了kobj->kset,则调用kobj_kset_join将kobj加入到kobj->kset中。同时,如果kobj->parent仍为NULL,则将kobj->parent设置为kobj->kset->kobj。然后,调用create_dir(kobj)在/sys目录下建立kobject相关目录结构。kobj_kset_join函数定义如下:[cpp] view plaincopyprint?
- static void kobj_kset_join(struct kobject *kobj)
{ - if (!kobj->kset)
return; -
kset_get(kobj->kset); - spin_lock(&kobj->kset->list_lock);
list_add_tail(&kobj->entry, &kobj->kset->list); - spin_unlock(&kobj->kset->list_lock);
- }
/* add the kobject to its kset's list */
/* add the kobject to its kset's list */static void kobj_kset_join(struct kobject *kobj){ if (!kobj->kset) return; kset_get(kobj->kset); spin_lock(&kobj->kset->list_lock); list_add_tail(&kobj->entry, &kobj->kset->list); spin_unlock(&kobj->kset->list_lock);}
create_dir函数定义如下:[cpp] view plaincopyprint?
- {
int error = 0; - if (kobject_name(kobj)) {
error = sysfs_create_dir(kobj); - if (!error) {
error = populate_dir(kobj); - if (error)
sysfs_remove_dir(kobj); - }
} - return error;
- }
static int create_dir(struct kobject *kobj)
static int create_dir(struct kobject *kobj){ int error = 0; if (kobject_name(kobj)) { error = sysfs_create_dir(kobj); if (!error) { error = populate_dir(kobj); if (error) sysfs_remove_dir(kobj); } } return error;}
首先调用sysfs_create_dir在/sys下建立目录,然后再调用populate_dir在新建目录下生成属性文件。sysfs_create_dir函数定义如下:[cpp] view plaincopyprint?
- * sysfs_create_dir - create a directory for an object.
* @kobj: object we're creating directory for. - */
int sysfs_create_dir(struct kobject * kobj) - {
enum kobj_ns_type type; - struct sysfs_dirent *parent_sd, *sd;
const void *ns = NULL; - int error = 0;
- BUG_ON(!kobj);
- if (kobj->parent)
parent_sd = kobj->parent->sd; - else
parent_sd = &sysfs_root; -
if (sysfs_ns_type(parent_sd)) - ns = kobj->ktype->namespace(kobj);
type = sysfs_read_ns_type(kobj); -
error = create_dir(kobj, parent_sd, type, ns, kobject_name(kobj), &sd); - if (!error)
kobj->sd = sd; - return error;
- }
/**
/** * sysfs_create_dir - create a directory for an object. * @kobj: object we're creating directory for. */int sysfs_create_dir(struct kobject * kobj){ enum kobj_ns_type type; struct sysfs_dirent *parent_sd, *sd; const void *ns = NULL; int error = 0; BUG_ON(!kobj); if (kobj->parent) parent_sd = kobj->parent->sd; else parent_sd = &sysfs_root; if (sysfs_ns_type(parent_sd)) ns = kobj->ktype->namespace(kobj); type = sysfs_read_ns_type(kobj); error = create_dir(kobj, parent_sd, type, ns, kobject_name(kobj), &sd); if (!error) kobj->sd = sd; return error;}
这里主要是通过调用create_dir函数建立kobject对应的目录。这个函数我们就不继续向下跟踪了。下面来看populate_dir函数,其定义如下:[cpp] view plaincopyprint?
- * populate_dir - populate directory with attributes.
* @kobj: object we're working on. - *
* Most subsystEMS have a set of default attributes that are associated - * with an object that registers with them. This is a helper called during
* object registration that loops through the default attributes of the - * subsystem and creates attributes files for them in sysfs.
*/ - static int populate_dir(struct kobject *kobj)
{ - struct kobj_type *t = get_ktype(kobj);
struct attribute *attr; - int error = 0;
int i; -
if (t && t->default_attrs) { - for (i = 0; (attr = t->default_attrs) != NULL; i++) {
error = sysfs_create_file(kobj, attr);- if (error)
break;- }
}- return error;
- }
- if (error)
/*
/* * populate_dir - populate directory with attributes. * @kobj: object we're working on. * * Most subsystems have a set of default attributes that are associated * with an object that registers with them. This is a helper called during * object registration that loops through the default attributes of the * subsystem and creates attributes files for them in sysfs. */static int populate_dir(struct kobject *kobj){ struct kobj_type *t = get_ktype(kobj); struct attribute *attr; int error = 0; int i; if (t && t->default_attrs) { for (i = 0; (attr = t->default_attrs) != NULL; i++) { error = sysfs_create_file(kobj, attr); if (error) break; } } return error;}
该函数循环遍历kobject的所有属性,并调用sysfs_create_file函数在/sys系统对应目录下建立属性文件。至此,kobject的注册过程我们就分析完了。kobject的注销过程是调用kobject_del函数,该函数定义如下:[cpp] view plaincopyprint?
- * kobject_del - unlink kobject fROM hierarchy.
* @kobj: object. - */
void kobject_del(struct kobject *kobj) - {
if (!kobj) - return;
- sysfs_remove_dir(kobj);
kobj->state_in_sysfs = 0; - kobj_kset_leave(kobj);
kobject_put(kobj->parent); - kobj->parent = NULL;
- }
/**
/** * kobject_del - unlink kobject from hierarchy. * @kobj: object. */void kobject_del(struct kobject *kobj){ if (!kobj) return; sysfs_remove_dir(kobj); kobj->state_in_sysfs = 0; kobj_kset_leave(kobj); kobject_put(kobj->parent); kobj->parent = NULL;}
这里需要注意的是,只要把目录删除,目录下的属性文件自动就删除了。
