C语言函数调用分析
首先push %ebp,是将调用函数的栈帧基地址压入栈中,也就是保存调用函数的栈帧EBP。将其指向的地址压入堆栈中。mov %esp,%ebp则是将ESP和EBP指向同一个地址,作为被调用函数的栈帧基地址。sub $0x18,%esp则是修改ESP的值,与EBP构成当前被调用函数的栈帧空间。
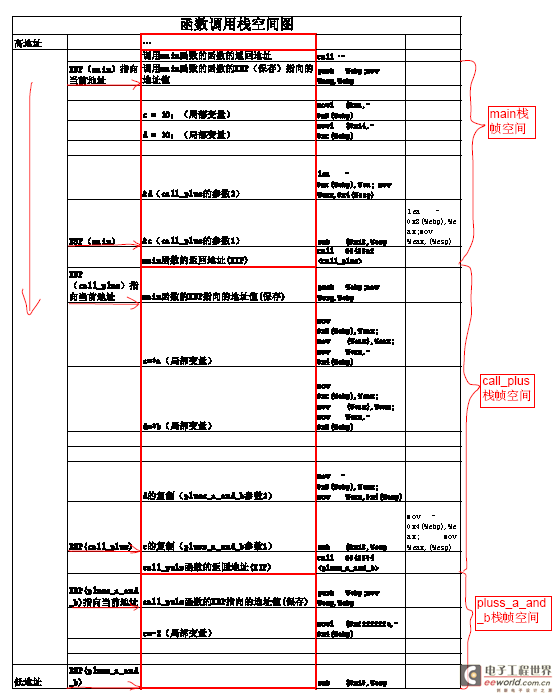
从图中可以每个函数的栈空间都是相互独立的,但是每一个栈空间的基本结构都是相同的。都是该函数的EBP指针,然后是局部变量空间,然后是往下一个函数的传递参数空间,返回的EBP地址。这样就能实现不同函数的调用,然后传递参数是采用基于EBP指针的相对位置实现的,并没有绝对地址。
由此可以知道栈空间的分布是根据调用情况分析的,当调用过多时就会导致溢出错误,因此并不是一味的迭代和递归。
关于函数调用的返回都是采用EAX寄存器实现的,但是当返回的是结构体以及联合体时返回就不能采用EAX实现了,基本的实现方法也是基于堆栈的。
- #include
- typedef struct{
- doubled;
- float f;
- inti;
- char c;
- }return_value;
- return_value my_test_of_return()
- {
- return_value rv;
- rv.d=12.56;
- rv.f=3.1;
- rv.i=10;
- rv.c=a;
- return rv;
- }
- intmain()
- {
- return_value local=my_test_of_return();
- return 0;
- }
编译以及反汇编以后得到如下的结果:
[gong@Gong-Computer deeplearn]$ gcc -g structpass.c -o structpass
[gong@Gong-Computer deeplearn]$ objdump -S -d structpass > structpass_s
- ...
- 08048394
: - char c;
- }return_value;
- return_value my_test_of_return()
- {
- 8048394: 55 push %ebp
- 8048395: 89 e5 mov %esp,%ebp
- 8048397: 83 ec 20 sub $0x20,%esp
- 804839a: 8b 45 08 mov 0x8(%ebp),%eax
- return_value rv;
- rv.d = 12.56;
- 804839d: dd 05 d8 84 04 08 fldl 0x80484d8
- 80483a3: dd 5d e8 fstpl -0x18(%ebp)
- rv.f = 3.1;
- 80483a6: ba 66 66 46 40 mov $0x40466666,%edx
- 80483ab: 89 55 f0 mov %edx,-0x10(%ebp)
- rv.i = 10;
- 80483ae: c7 45 f4 0a 00 00 00 movl $0xa,-0xc(%ebp)
- rv.c = a;
- 80483b5: c6 45 f8 61 movb $0x61,-0x8(%ebp)
- return rv;
- 80483b9: 8b 55 e8 mov -0x18(%ebp),%edx
- 80483bc: 89 10 mov %edx,(%eax)
- 80483be: 8b 55 ec mov -0x14(%ebp),%edx
- 80483c1: 89 50 04 mov %edx,0x4(%eax)
- 80483c4: 8b 55 f0 mov -0x10(%ebp),%edx
- 80483c7: 89 50 08 mov %edx,0x8(%eax)
- 80483ca: 8b 55 f4 mov -0xc(%ebp),%edx
- 80483cd: 89 50 0c mov %edx,0xc(%eax)
- 80483d0: 8b 55 f8 mov -0x8(%ebp),%edx
- 80483d3: 89 50 10 mov %edx,0x10(%eax)
- }
- 80483d6: c9 leave
- 80483d7: c2 04 00 ret $0x4
- 080483da
: - int main()
- {
- 80483da: 8d 4c 24 04 lea 0x4(%esp),%ecx
- 80483de: 83 e4 f8 and $0xfffffff8,%esp
- 80483e1: ff 71 fc pushl -0x4(%ecx)
- 80483e4: 55 push %ebp
- 80483e5: 89 e5 mov %esp,%ebp
- 80483e7: 51 push %ecx
- 80483e8: 83 ec 2c sub $0x2c,%esp
- return_value local = my_test_of_return();
- 80483eb: 8d 45 e0 lea -0x20(%ebp),%eax
- 80483ee: 89 04 24 mov %eax,(%esp)
- 80483f1: e8 9e ff ff ffcall8048394
- 80483f6: 83 ec 04 sub $0x4,%esp
- return 0;
- 80483f9: b8 00 00 00 00 mov $0x0,%eax
- }
- 80483fe: 8b 4d fc mov -0x4(%ebp),%ecx
- 8048401: c9 leave
- 8048402: 8d 61 fc lea -0x4(%ecx),%esp
- ...
从上面的结果可以知道可以知道,返回的过程并不是一次通过EAX返回的,而是通过堆栈一个一个的传递出来,实现结果的返回。因此这也是我们需要注意的地方。
同样对于结构体的传递方式也是采用堆栈的方式进行传递,基本的参看下面的分析。参数也是依据堆栈中的位置进行控制的。
代码:
- #include
- typedef struct{
- doubled;
- float f;
- inti;
- char c;
- }return_value;
- return_value my_test_pass(return_value pass)
- {
- return_value rv;
- rv.d=pass.d;
- rv.f=pass.f;
- rv.i=pass.i;
- rv.c=pass.c;
- return rv;
- }
- return_value my_test_of_return()
- {
- return_value rv;
- rv.d=12.56;
- rv.f=3.1;
- rv.i=10;
- rv.c=a;
- return rv;
- }
- intmain()
- {
- return_value local=my_test_of_return();
- return_value local1=my_test_pass(local);
- return 0;
- }
编译和反汇编过程:
[gong@Gong-Computer deeplearn]$ gcc -g structpass.c -o structpass
[gong@Gong-Computer deeplearn]$ objdump -S -d structpass > structpass_s
- ...
- int main()
- {
- 804841d: 8d 4c 24 04 lea 0x4(%esp),%ecx
- 8048421: 83 e4 f8 and $0xfffffff8,%esp
- 8048424: ff 71 fc pushl -0x4(%ecx)
- 8048427: 55 push %ebp
- 8048428: 89 e5 mov %esp,%ebp
- 804842a: 51 push %ecx
- 804842b: 83 ec
C语言函数调 相关文章:
- Windows CE 进程、线程和内存管理(11-09)
- RedHatLinux新手入门教程(5)(11-12)
- uClinux介绍(11-09)
- openwebmailV1.60安装教学(11-12)
- Linux嵌入式系统开发平台选型探讨(11-09)
- Windows CE 进程、线程和内存管理(二)(11-09)
