Simple Power Monitor
时间:04-11
来源:互联网
点击:
Systems in which an analog-digital converter (ADC) monitors the supply voltage must contend with the condition in which the ADC reference is usually lower than the supply voltage (Figure 1). An external resistor-divider can pull the supply voltage within the ADC's range, but even 0.1% resistors introduce an error that may be objectionable in certain applications.
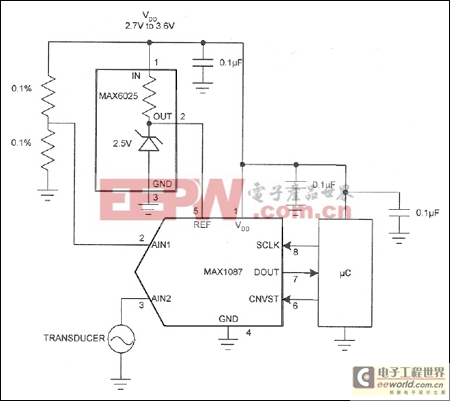
Figure 1. A supply-monitoring circuit like the one shown here usually requires that the ADC input be lower than the reference voltage. Consequently the circuit must include a resistive divider (and associated error) at the ADC input.
One solution to the ADC reference voltage problem is simply to eliminate the divider (Figure 2). You can relate the reference to the supply voltage by connecting the supply voltage as a reference, and the reference (2.500V for the A) to an input. As Figure 2 shows for the MAX1087, the ADC must be capable of accepting an external reference as high as the supply voltage. The other channels are now measured as a ratio to the supply voltage instead of the reference, but software can correct that problem.
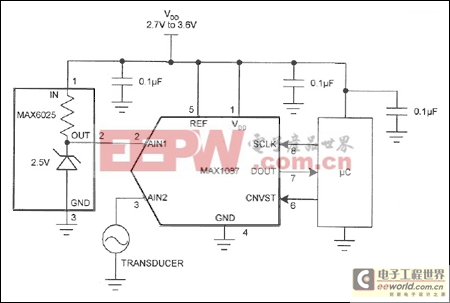
Figure 2. The connections shown enable this ADC (which allows VIN to be as high as the reference) to monitor supply voltage without the divider included in Figure 1.
Because the supply rail serves as a reference, any noise on the rail disturbs all channels. You may, therefore, need to add a local lowpass filter to quiet the supply voltage in noisy environments.

Figure 1. A supply-monitoring circuit like the one shown here usually requires that the ADC input be lower than the reference voltage. Consequently the circuit must include a resistive divider (and associated error) at the ADC input.
One solution to the ADC reference voltage problem is simply to eliminate the divider (Figure 2). You can relate the reference to the supply voltage by connecting the supply voltage as a reference, and the reference (2.500V for the A) to an input. As Figure 2 shows for the MAX1087, the ADC must be capable of accepting an external reference as high as the supply voltage. The other channels are now measured as a ratio to the supply voltage instead of the reference, but software can correct that problem.

Figure 2. The connections shown enable this ADC (which allows VIN to be as high as the reference) to monitor supply voltage without the divider included in Figure 1.
Because the supply rail serves as a reference, any noise on the rail disturbs all channels. You may, therefore, need to add a local lowpass filter to quiet the supply voltage in noisy environments.
模拟电源 电源管理 模拟器件 模拟电子 模拟 模拟电路 模拟芯片 德州仪器 放大器 ADI 相关文章:
- 采用数字电源还是模拟电源?(01-17)
- 模拟电源管理与数字电源管理(02-05)
- 数字电源正在超越模拟电源(03-19)
- 数字电源PK模拟电源(04-03)
- TI工程师现身说法:采用数字电源还是模拟电源?(10-10)
- 开关电源与模拟电源的分别(05-08)
