手机耳机接口插拔识别方案
The audio jack has become standard in smart phone applications.These jacks allow the user to either plug a headset with a microphone (4 pole) or stereo headphones (3 pole).The current system design allows the mobile phone to detect between 3 or 4 pole and Send/End key, but the design has inherent issues with power, detection errors, and pop-n-click.These issues in functionality and audio quality can result in a poor user experience.Fairchild’s new audio jack detection switches provide an interface between the audio jack, baseband processor, and microphone preamp.These new devices automatically detect what is plugged into the audio jack, resolve software issues, drastically reduce system current, reduces PCB space, and eliminate pop-n-click caused by the microphone bias.
The Current Solution:
The current audio jack detection solution is designed with discrete components, typically a comparator with supporting resistors and capacitors (see Figure 1).This design has inherent flaws, these flaws result in user interface issues wasted current, and audio pop-n-click.The comparator in the circuit is utilized for two functions; one to detect between a 3 pole (stereo headphones) or 4 pole (headset with microphone) audio plug, two detect a Send/End key push.If a 3 pole plug is inserted the mic line is pulled to GND, the comparator outputs a Low to the baseband.When a 4 pole plug is connected the mic line typically is 1.8V with no Send/End key press.When the Send/End key is pressed it shorts the mic line to ground and the comparator outputs a s Low to the baseband.This causes a fundamental issue if a 4 pole headset is connected while pushing the Send/End key the baseband registers a 3 Pole jack, and the system may never recover.Additionally, this design increases current consumption in two significant areas.The resistor divider used to set the comparators voltage reference is connected directly to the supply, which continuously drains about 28μA (I2 on Figure 1) even when there is no audio plug.The Mic bias is not isolated based on the system settings.If a 4 pole plug is connected and the mic is not required the Mic bias drains >500uA (I1 on Figure 1) through the RMIC and Microphone.Not gating the Mic bias also creates a pop-n-click issue.The mic line is typically the fourth pole in the audio jack, when the plug is inserted or removed the left and right speaker terminals scrape across the mic bias, causing pop-n-click.All of these issues cause increased system design & software time to try to mitigate them, and a poor user experience.
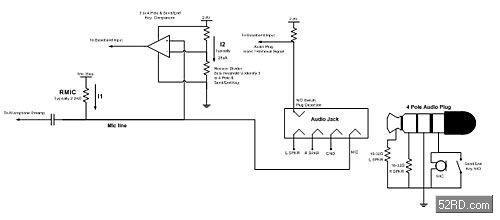
Figure 1 – Current Audio Jack Detection Design
Audio Jack Detection Switches:
Mobile phone manufacturers increased scrutiny on the user experience has resulted in a new device function; audio jack detection switches.Devices such as the FSA8008 interface between the audio jack, baseband, mic preamp (Figure 2).These detection switches focus on resolving the issues of the current solution, while providing further features such as: board space savings, increased ESD performance, simple baseband interfaces, and automatic reset.
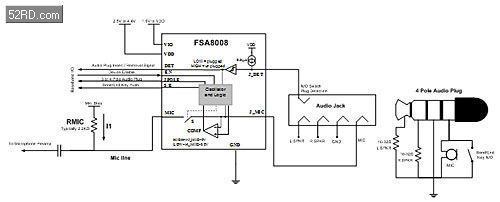
Figure 2 – Audio Jack Detection Switch Solution
Solve Stuck Send/End Key Issue:
When a user plugs in a headset and holds the Send/End key the phone errors and recognizes a 4 pole headset as a 3 pole stereo headphones.In this mode the mic preamp will be muted or off and the headset microphone will not function.Further, the phone will never recover from this state creating a poor user experience.Audio jack detection swi
- T-DMB推动手机电视市场崛起(08-15)
- 手机电视的技术(08-19)
- 全球手机电视三大技术标准对比分析(08-19)
- 发展普遍看好 手机电视正在崛起中的新兴媒体(08-25)
- 基于T-DMB标准的手机电视解决方案(08-25)
- 手机电视国标CMMB将进入测试阶段 年底可出台(08-26)
