Powerpc构架系统内核和内核模块调试
后,系统的的调试信息简单的通过CONFIG_DEBUG_INFO宏来控制了,那么CONFIG_DEBUG_INFO宏又是从哪里来的呢?它其实是从内核的配置文件.config里面来的。
一般内核通过make menuconfig做配置的时候,都有
Kernel hacking --->
[*] Kernel debugging
[*] Compile the kernel with debug info
[*] Force gcc to inline functions marked 'inline' (2.6比较新的内核有这一项)
[*] Include BDI-2000 user context switcher (有的系统直接提供了这个选项,它和BDI2000的PTBASE设置配合)
通过保存后,以上选项会生成如下配置选项:
CONFIG_DEBUG_KERNEL=y
CONFIG_DEBUG_INFO=y
CONFIG_FORCED_INLINING=y
CONFIG_BDI_SWITCH=y
值得关注的是PowerPC内核中CONFIG_BDI_SWITCH,它到底在内核中怎样起作用的?
我们看arch/powerpc/kernel/head_32.S的关键代码:
…
/* Load up the kernel Context */
2: bl load_up_mmu
#ifdef CONFIG_BDI_SWITCH
/* Add helper information for the Abatron bdiGDB debugger.
* We do this here because we know the mmu is disabled, and
* will be enabled for real in just a few instructions.
*/
lis r5, abatron_pteptrs@h
ori r5, r5, abatron_pteptrs@l
stw r5, 0xf0(r0)??? /* This much match your Abatron config */
lis r6, swapper_pg_dir@h
ori r6, r6, swapper_pg_dir@l
tophys(r5, r5)
stw r6, 0(r5)
#endif /* CONFIG_BDI_SWITCH */
/* Now turn on the MMU for real! */
…
它在MMU真正时能之前先增加了BDI2000帮助信息。在arch/powerpc/kernel/head_32.S的最后通过abatron_pteptrs保留了8个自己的空间给BDI2000用于保存2个页表指针,如下:
/* Room for two PTE pointers, usually the kernel and current user pointers
* to their respective root page table.
*/
abatron_pteptrs:
.space 8
3. 内核调试
通过以上的准备工作,就可以进行内核和模块的调试了,内核调试步骤如下:
说明:下面的步骤中
8349E-mITX-GP> 表示BDI2000的命令行窗口
[root@newhost misc-modules]# 表示开发主机
DDD> 或GDB> 表示是开发主机上的DDD的调试窗口中
root@mpc8349emitxgp:~# 表示目标系统中
1. 获取恰当的断点设置位置:
[shyi@newhost pro50_mpc8349_kernel]$ cat System.map |grep start_kernel
c03b05dc T start_kernel #得到start_kernel的虚拟地址
2.设置断点,加载内核,启动DDD的连接
8349E-mITX-GP>reset
8349E-mITX-GP>halt
8349E-mITX-GP>bi 0xc03b05dc (这个值是由System.map中的start_kernel的地址而来的)
8349E-mITX-GP>go
- TARGET: stopped #提示系统进入断点了
8349E-mITX-GP>info
Target CPU : MPC83xx (e300c1)
Target state : debug mode
Debug entry cause : instruction address breakpoint
Current PC : 0xc03b05dc
Current CR : 0x44044022
Current MSR : 0x00001032
Current LR : 0x00003438
8349E-mITX-GP>
# 这时串口可看打到打印信息如:
Uncompressing Kernel Image ... OK
Booting using the fdt at 0xc00000
Loading Device Tree to 007fc000, end 007fefff ... OK
图形系统中启动DDD
[root@newhost scull]# cd /opt/pro50/montavista/pro/devkit/ppc/83xx/target/root/examples/misc-Modules
[root@newhost misc-modules]# ddd --debugger ppc_83xx-gdb –gdb /home/shyi/workspace/pro50_mpc8349_kernel/vmlinux
(gdb)target remote 192.168.7.64:2001 (其中192.168.7.64:2001为BDI2000的IP和调试端口)
8349E-mITX-GP>ci
8349E-mITX-GP>break soft #改变为软断点方式
这时候可以在DDD>图形界面里面最右边点击鼠标右键来设置断点,如图:
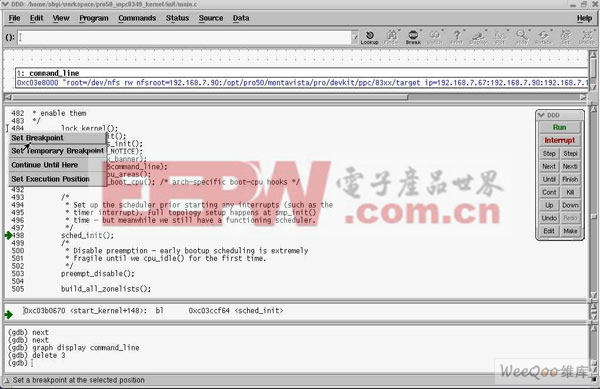
(注意:系统有些地方不能停住,需要在合适的位置来设置断点)
(gdb)cont
这时候系统就会停止在断点设置的地方,接下来就可以进行内核断点调试了,如下图:

4.内核模块的调试
使用LDD3的jit.c模块进行调试的演示,DDD(或者说GDB)GDB的初始化脚本放置在~/.gdbinit:
其中.gdbinit的内容如下:
define lsmod
printf AddressttModulen
set $m=(struct list_head *)modules
set $done=0
while ( !$done )
# list_head is 4-bytes into struct module
set $mp=(struct module *)((char *)$m->next - (char *)4)
printf 0x%08Xt%sn, $mp, $mp->name
if ($mp->list->next == modules)
set $done=1
end
set $m=$m->next
end
end
define addmodulesymbols
set $myModule=(struct module*) $arg0
set $myAddr=$myMo
- VXWORKS内核分析(11-11)
- linux内核编译步骤(11-11)
- Linux内核解读入门(11-09)
- Linux内核编译过程详解(kernel2.6.7) (04-16)
- 嵌入式Linux内核移植相关代码分析(04-21)
- 什么是module 以及如何写一个module(转)(04-23)
