第17章 ComplexMathFunctions的使用(一)
第17章 ComplexMathFunctions的使用(一)
本期教程主要讲解复数运算中的共轭,点乘和模的求解(什么是复数,大家应该还有印象吧,这个很重要,在后面FFT等算法的处理时都要用到,印象不深的同学需要简单的补充下高数知识)。
17.1 复数共轭运算 ComplexConj
17.2 复数点乘ComplexDotProduct
17.3 复数求模ComplexMag
17.4 总结
17.1 复数共轭运算 ComplexConj
17.1.1 arm_cmplx_conj_f32
公式描述:
for(n=0;n<numSamples; n++)
{
pDst[(2*n)+0)] = pSrc[(2*n)+0]; // 实部
pDst[(2*n)+1)] = -pSrc[(2*n)+1]; // 虚部
}
函数定义如下:
voidarm_cmplx_conj_f32(float32_t * pSrc, float32_t * pDst, uint32_t numSamples)
参数定义:
*pSrc points to the input vector
*pDst points to the output vector
numSamples number of complex samples in each vector
注意事项:
1. 数组pSrc中存储的数据格式是(实部,虚部,实部,虚部……………),一定要按照这个顺序存储数据,比如数据1-j,j,2+3j这个三个数在数组中的存储格式就是:pSrc[6] = {1, -1, 0, 1, 2, 3}。(注意第三个数据是0)。函数的输出结果pDst也是按照这个顺序存储的。
17.1.2 arm_cmplx_conj_q31
公式描述:
for(n=0;n<numSamples; n++)
{
pDst[(2*n)+0)] = pSrc[(2*n)+0]; // 实部
pDst[(2*n)+1)] = -pSrc[(2*n)+1]; // 虚部
}
函数定义如下:
voidarm_cmplx_conj_q31(q31_t * pSrc, q31_t * pDst, uint32_t numSamples)
参数定义:
*pSrc points to the input vector
*pDst points to the output vector
numSamples number of complex samples in each vector
注意事项:
1. 数组pSrc中存储的数据格式是(实部,虚部,实部,虚部……………),一定要按照这个顺序存储数据,比如数据1-j,j,2+3j这个三个数在数组中的存储格式就是:pSrc[6] = {1, -1, 0, 1, 2, 3}。(注意第三个数据是0)。函数的输出结果pDst也是按照这个顺序存储的。
2. 这个函数使用了饱和运算。
3. 数值0x80000000由于饱和运算将变成0x7FFFFFFF。
17.1.3 arm_cmplx_conj_q15
公式描述:
for(n=0;n<numSamples; n++)
{
pDst[(2*n)+0)] = pSrc[(2*n)+0]; // 实部
pDst[(2*n)+1)] = -pSrc[(2*n)+1]; // 虚部
}
函数定义如下:
voidarm_cmplx_conj_q15(q15_t * pSrc, q15_t * pDst, uint32_t numSamples)
参数定义:
*pSrc points to the input vector
*pDst points to the output vector
numSamples number of complex samples in each vector
注意事项:
1. 数组pSrc中存储的数据格式是(实部,虚部,实部,虚部……………),一定要按照这个顺序存储数据,比如数据1-j,j,2+3j这个三个数在数组中的存储格式就是:pSrc[6] = {1, -1, 0, 1, 2, 3}。(注意第三个数据是0)。函数的输出结果pDst也是按照这个顺序存储的。
2. 这个函数使用了饱和运算。
3. 数值0x8000由于饱和运算将变成0x7FFF。
17.1.4 实例讲解
实验目的:
1. 学习ComplexMathFunctions中复数共轭的求解(首先大家要明白什么是复数共轭)
实验内容:
1. 按下按键K1, 串口打印函数DSP_CONJ的输出结果
实验现象:
通过窗口上位机软件SecureCRT(V5光盘里面有此软件)查看打印信息现象如下:
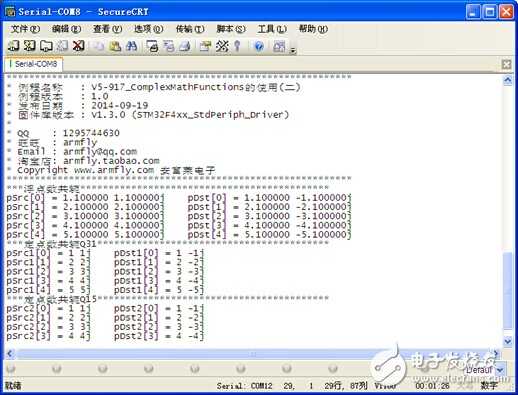
程序设计:
- /*
- *********************************************************************************************************
- * 函 数 名: DSP_CONJ
- * 功能说明: 浮点数复数共轭
- * 形 参:无
- * 返 回 值: 无
- *********************************************************************************************************
- */
- static void DSP_CONJ(void)
- {
- uint8_t i;
- float32_t pSrc[10] = {1.1f, 1.1f, 2.1f, 2.1f, 3.1f, 3.1f, 4.1f, 4.1f, 5.1f, 5.1f};
- float32_t pDst[10];
-
- q31_t pSrc1[10] = {1, 1, 2, 2, 3, 3, 4, 4, 5, 5};
- q31_t pDst1[10];
-
- q15_t pSrc2[10] = {1, 1, 2, 2, 3, 3, 4, 4, 5, 5};
- q15_t pDst2[10];
-
- /***浮点数共轭*******************************************************************************/
- arm_cmplx_conj_f32(pSrc, pDst, 5);
- printf("***浮点数共轭********************************************\r\n");
- for(i = 0; i < 5; i++) (1)
- {
- printf("pSrc[%d] = %f %fj pDst[%d] = %f %fj\r\n", i, pSrc[2*i], pSrc[2*i+1], i, pDst[2*i],
- pDst[2*i+1]);
- }
-
- /***定点数共轭Q31*******************************************************************************/
- printf("***定点数共轭Q31*****************************************\r\n"); (2)
- arm_cmplx_conj_q31(pSrc1, pDst1, 5);
- for(i = 0; i < 5; i++)
- {
- printf("pSrc1[%d] = %d %dj pDst1[%d] = %d %dj\r\n", i, pSrc1[2*i], pSrc1[2*i+1], i, pDst1[2*i], pDst1[2*i+1]);
- }
-
- /***定点数共轭Q15*******************************************************************************/
- printf("***定点数共轭Q15*****************************************\r\n");
- arm_cmplx_conj_q15(pSrc2, pDst2, 5);
-
- for(i = 0; i < 5; i++) (3)
- {
- printf("pSrc2[%d] = %d %dj pDst2[%d] = %d %dj\r\n", i, pSrc2[2*i], pSrc2[2*i+1], i, pDst2[2*i], pDst2[2*i+1]);
- }
- }
1. 这里先简单的普及一下复数共轭的基础知识,可能很多人都已经忘记了(来自wiki百科):
在数学中,复数的复共轭(常简称共轭)是对虚部变号的运算,因此一个复数
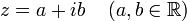
的复共轭是
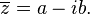
举例明之:
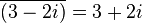
![]()
在复数的极坐标表法下,复共轭写成
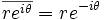
这点可以透过欧拉公式验证
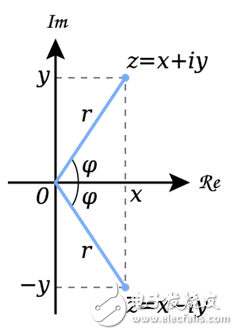
将复数理解为复平面,则复共轭无非是对实轴的反射。复数![]()
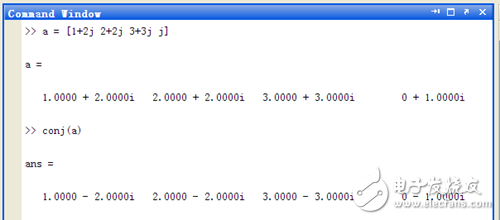
下面再说一下如何在matlab上面共轭复数。比如我们要求解数组a = [1+2j 2+2j 3+3j j]的共轭复数:
2. Q31格式定点数的共轭求解。
3. Q15格式定点数的共轭求解。
17.2 复数点乘ComplexDotProduct
17.2.1 arm_cmplx_dot_prod_f32
公式描述:
realResult=0;
imagResult=0;
for(n=0;n<numSamples; n++) {
realResult += pSrcA[(2*n)+0]*pSrcB[(2*n)+0] -pSrcA[(2*n)+1]*pSrcB[(2*n)+1];
imagResult += pSrcA[(2*n)+0]*pSrcB[(2*n)+1] +pSrcA[(2*n)+1]*pSrcB[(2*n)+0];
}
函数定义如下:
voidarm_cmplx_dot_prod_f32(float32_t * pSrcA, float32_t * pSrcB, uint32_tnumSamples,
float32_t * realResult, float32_t * imagResult)
参数定义:
*pSrcA points to the first input vector
*pSrcB points to the second input vector
numSamples number of complex samples in each vector
*realResult real part of the result returned here
*imagResult imaginary part of the result returnedhere
注意事项:
1. 数组pSrc和pDst中存储的数据格式是(实部,虚部,实部,虚部……………),一定要按照这个顺序存储数据,比如数据1-j,j,2+3j这个三个数在数组中的存储格式就是:pSrc[6] = {1, -1, 0, 1, 2, 3}。(注意第三个数据是0)。输出结果的实部和虚部是分开的。
17.2.2 arm_cmplx_dot_prod_q31公式描述:
realResult=0;
imagResult=0;
for(n=0;n<numSamples; n++) {
realResult += pSrcA[(2*n)+0]*pSrcB[(2*n)+0] -pSrcA[(2*n)+1]*pSrcB[(2*n)+1];
imagResult += pSrcA[(2*n)+0]*pSrcB[(2*n)+1] +pSrcA[(2*n)+1]*pSrcB[(2*n)+0];
}
函数定义如下:
voidarm_cmplx_dot_prod_q31(q31_t * pSrcA, q31_t * pSrcB, uint32_t numSamples,
q63_t * realResult,q63_t * imagResult)
参数定义:
*pSrcA points to the first input vector
*pSrcB points to the second input vector
numSamples number of complex samples in each vector
*realResult real part of the result returned here
*imagResult imaginary part of the result returnedhere
注意事项:
1. 这个函数的内部使用了64累加器,1.31格式数据乘以1.31格式数据结果就是2.62格式,这里我们将所得结果右移14位,那么数据就是16.48格式。由于加数是不支持饱和运算,所以只要numSamples的个数小于32768就不会有溢出的危险。
2. 数组pSrc和pDst中存储的数据格式是(实部,虚部,实部,虚部……………),一定要按照这个顺序存储数据,比如数据1-j,j,2+3j这个三个数在数组中的存储格式就是:pSrc[6] = {1, -1, 0, 1, 2, 3}。(注意第三个数据是0)。输出结果的实部和虚部是分开的。
17.2.3 arm_cmplx_dot_prod_q15公式描述:
realResult=0;
imagResult=0;
for(n=0; n<numSamples;n++) {
realResult += pSrcA[(2*n)+0]*pSrcB[(2*n)+0] -pSrcA[(2*n)+1]*pSrcB[(2*n)+1];
imagResult += pSrcA[(2*n)+0]*pSrcB[(2*n)+1] +pSrcA[(2*n)+1]*pSrcB[(2*n)+0];
}
函数定义如下:
voidarm_cmplx_dot_prod_q15(q15_t * pSrcA, q15_t * pSrcB, uint32_t numSamples,
q31_t *realResult, q31_t * imagResult)
参数定义:
*pSrcA points to the first input vector
*pSrcB points to the second input vector
numSamples number of complex samples in each vector
*realResult real part of the result returned here
*imagResult imaginary part of the result returnedhere
注意事项:
1. 这个函数的内部使用了64累加器,1.31格式数据乘以1.31格式数据结果就是2.62格式,这里我们将所得结果右移14位,那么数据就是16.48格式。由于加数是不支持饱和运算,所以只要numSamples的个数小于32768就不会有溢出的危险。
2. 数组pSrc和pDst中存储的数据格式是(实部,虚部,实部,虚部……………),一定要按照这个顺序存储数据,比如数据1-j,j,2+3j这个三个数在数组中的存储格式就是:pSrc[6] = {1, -1, 0, 1, 2, 3}。(注意第三个数据是0)。输出结果的实部和虚部是分开的。
17.2.4 实例讲解实验目的:
1. 学习ComplexMathFunctions中复数点乘的实现
实验内容:
1. 按下按键K2, 串口打印函数DSP_CmplxDotProduct的输出结果
实验现象:
通过窗口上位机软件SecureCRT(V5光盘里面有此软件)查看打印信息现象如下:
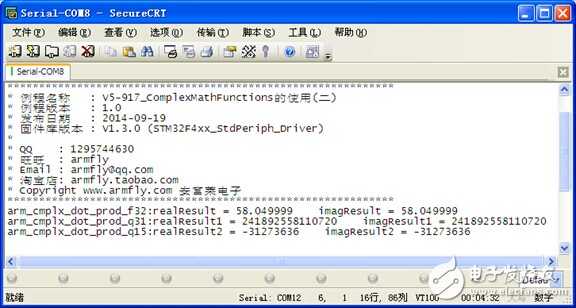
程序设计:
- /*
- *********************************************************************************************************
- * 函 数 名: DSP_CmplxDotProduct
- * 功能说明: 浮点数cos和sin计算
- * 形 参:无
- * 返 回 值: 无
- *********************************************************************************************************
- */
- static void DSP_CmplxDotProduct(void)
- {
- uint8_t i;
- float32_t pSrcA[10] = {1.1f, 1.1f, 2.1f, 2.1f, 3.1f, 3.1f, 4.1f, 4.1f, 5.1f, 5.1f};
- float32_t pSrcB[10] = {1.1f, 1.1f, 2.1f, 2.1f, 3.1f, 3.1f, 4.1f, 4.1f, 5.1f, 5.1f};
- float32_t realResult;
- float32_t imagResult;
-
- q31_t pSrcA1[10] = {1*268435456, 1*268435456, 2*268435456, 2*268435456, 3*268435456, 3*268435456,
- 4*268435456, 4*268435456, 5*268435456, 5*268435456};
- q31_t pSrcB1[10] = {1*268435456, 1*268435456, 2*268435456, 2*268435456, 3*268435456, 3*268435456,
- 4*268435456, 4*268435456, 5*268435456, 5*268435456};
- q63_t realResult1;
- q63_t imagResult1;
-
- q15_t pSrcA2[10] = {5000, 10000, 15000, 20000, 25000, 5000, 10000, 15000, 20000, 25000};
- q15_t pSrcB2[10] = {5000, 10000, 15000, 20000, 25000, 5000, 10000, 15000, 20000, 25000};
- q31_t realResult2;
- q31_t imagResult2;
-
- /***浮点数点乘*******************************************************************************/
- arm_cmplx_dot_prod_f32(pSrcA, pSrcB, 5, &realResult, &imagResult); (1)
- printf("arm_cmplx_dot_prod_f32:realResult = %f imagResult = %f\r\n", realResult, imagResult);
-
- /***定点数点乘Q31*******************************************************************************/
- arm_cmplx_dot_prod_q31(pSrcA1, pSrcB1, 5, &realResult1, &imagResult1); (2)
- printf("arm_cmplx_dot_prod_q31:realResult1 = %lld imagResult1 = %lld\r\n", realResult1, imagResult1);
-
- /***定点数点乘Q15*******************************************************************************/
- arm_cmplx_dot_prod_q15(pSrcA2, pSrcB2, 5, &realResult2, &imagResult2); (3)
- printf("arm_cmplx_dot_prod_q15:realResult2 = %d imagResult2 = %d\r\n", realResult2, imagResult2);
- }
1. 讲解复数的点乘以前,要明白简单的复数乘法的实现,也就是前面的那个公式描述:
realResult=0;
imagResult=0;
for(n=0; n<numSamples;n++) {
realResult +=pSrcA[(2*n)+0]*pSrcB[(2*n)+0] - pSrcA[(2*n)+1]*pSrcB[(2*n)+1];
imagResult +=pSrcA[(2*n)+0]*pSrcB[(2*n)+1] + pSrcA[(2*n)+1]*pSrcB[(2*n)+0];
}
用代数式来表示复数乘法就是:
(a+bi)(c+di)=(ac-bd)+(ad+bc)i
这里求解的是浮点数的点乘。
2. Q31格式定点数的点乘。
3. Q15格式定点数的点乘。
17.3 复数求模 ComplexMag
17.3.1 arm_cmplx_mag_f32
公式描述:
for(n=0;n<numSamples; n++) {
pDst[n] = sqrt(pSrc[(2*n)+0]^2 +pSrc[(2*n)+1]^2);
}
函数定义如下:
voidarm_cmplx_mag_f32(float32_t * pSrc, float32_t * pDst, uint32_t numSamples)
参数定义:
*pSrcA points to the first input vector
*pSrcB points to the second input vector
numSamples number of complex samples in each vector
*realResult real part of the result returned here
*imagResult imaginary part of the result returnedhere
注意事项:
1. 数组pSrc和pDst中存储的数据格式是(实部,虚部,实部,虚部……………),一定要按照这个顺序存储数据,比如数据1-j,j,2+3j这个三个数在数组中的存储格式就是:pSrc[6] = {1, -1, 0, 1, 2, 3}。(注意第三个数据是0)。
17.3.2 arm_cmplx_mag_q31
公式描述:
for(n=0;n<numSamples; n++) {
pDst[n] = sqrt(pSrc[(2*n)+0]^2 +pSrc[(2*n)+1]^2);
}
函数定义如下:
voidarm_cmplx_mag_q31(q31_t * pSrc, q31_t * pDst, uint32_t numSamples)
参数定义:
*pSrc points to the complex input vector
*pDst points to the real output vector
numSamples numberof complex samples in the input vector
注意事项:
1. 数组pSrc和pDst中存储的数据格式是(实部,虚部,实部,虚部……………),一定要按照这个顺序存储数据,比如数据1-j,j,2+3j这个三个数在数组中的存储格式就是:pSrc[6] = {1, -1, 0, 1, 2, 3}。(注意第三个数据是0)。
2. 1.31格式的数据乘1.31格式的数据,并经过移位处理后结果是2.30格式。
17.3.3 arm_cmplx_mag_q15
公式描述:
for(n=0;n<numSamples; n++) {
pDst[n] = sqrt(pSrc[(2*n)+0]^2 +pSrc[(2*n)+1]^2);
}
函数定义如下:
voidarm_cmplx_mag_q31(q31_t * pSrc, q31_t * pDst, uint32_t numSamples)
参数定义:
*pSrc points to the complex input vector
*pDst points to the real output vector
numSamples numberof complex samples in the input vector
注意事项:
1. 数组pSrc和pDst中存储的数据格式是(实部,虚部,实部,虚部……………),一定要按照这个顺序存储数据,比如数据1-j,j,2+3j这个三个数在数组中的存储格式就是:pSrc[6] = {1, -1, 0, 1, 2, 3}。(注意第三个数据是0)。
2. 1.15格式的数据乘1.15格式的数据,并经过移位处理后结果是2.14格式。
17.3.4 实例讲解
实验目的:
1. 学习ComplexMathFunctions中复数的求模。
实验内容:
1. 按下按键K3, 串口打印函数DSP_CmplxMag的输出结果
实验现象:
通过窗口上位机软件SecureCRT(V5光盘里面有此软件)查看打印信息现象如下:
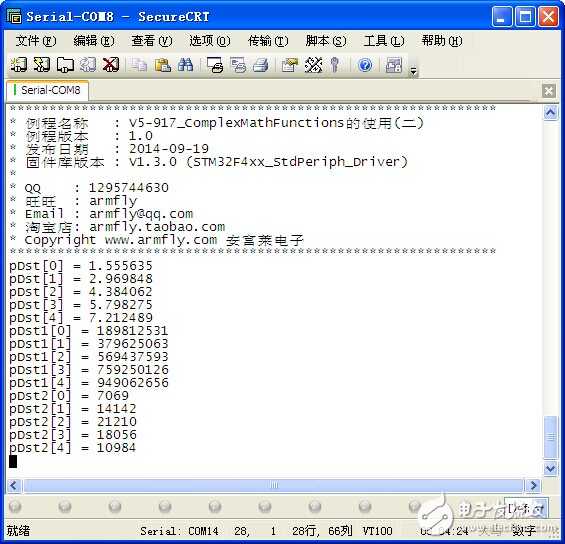
程序设计:
- /*
- *********************************************************************************************************
- * 函 数 名: DSP_CmplxMag
- * 功能说明: 浮点数cos和sin计算
- * 形 参:无
- * 返 回 值: 无
- *********************************************************************************************************
- */
- static void DSP_CmplxMag(void)
- {
- uint8_t i;
- float32_t pSrc[10] = {1.1f, 1.1f, 2.1f, 2.1f, 3.1f, 3.1f, 4.1f, 4.1f, 5.1f, 5.1f};
- float32_t pDst[10];
-
- q31_t pSrc1[10] = {1*268435456, 1*268435456, 2*268435456, 2*268435456, 3*268435456, 3*268435456,
- 4*268435456, 4*268435456, 5*268435456, 5*268435456};
- q31_t pDst1[10];
-
- q15_t pSrc2[10] = {5000, 10000, 15000, 20000, 25000, 5000, 10000, 15000, 20000, 25000};
- q15_t pDst2[10];
-
- /***浮点数求模*******************************************************************************/
- arm_cmplx_mag_f32(pSrc, pDst, 5); (1)
- for(i = 0; i < 5; i++)
- {
- printf("pDst[%d] = %f\r\n", i, pDst[i]);
- }
-
- /***定点数求模Q31*******************************************************************************/
- arm_cmplx_mag_q31(pSrc1, pDst1, 5); (2)
- for(i = 0; i < 5; i++)
- {
- printf("pDst1[%d] = %d\r\n", i, pDst1[i]);
- }
-
- /***定点数求模Q15*******************************************************************************/
- arm_cmplx_mag_q15(pSrc2, pDst2, 5); (3)
- for(i = 0; i < 5; i++)
- {
- printf("pDst2[%d] = %d\r\n", i, pDst2[i]);
- }
- }
1. 跟前面的求共轭和求点乘一样,先普及一下复数如何求模,用代数式表示就是:
a+bi,a和b是实数,则模就是|a+bi|=√(a2+b2)
这里求的是浮点数的模。
2. Q31格式定点数求模
3. Q15格式定点数求模
17.4 总结
本期教程就跟大家讲这么多,有兴趣的可以深入研究下算法的具体实现。
